Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of engineering and technology, Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) stand out as a remarkable innovation. These materials possess a unique ability to return to a predetermined shape when subjected to specific thermal conditions, making them invaluable in various applications. Among the diverse types of SMAs, Nitinol has gained prominence for its exceptional properties and versatility, particularly in SMA wire actuators.
Understanding Shape Memory Alloys
Shape Memory Alloys are metallic materials that can undergo significant deformation and revert to their original shape upon heating. This fascinating property is due to the phase transformation that occurs within the alloy’s microstructure, which is primarily composed of nickel and titanium in the case of Nitinol. The ability to harness these characteristics opens up a world of possibilities for creating innovative devices across multiple industries.
The Power of SMA Wire Actuators
SMA wire actuators leverage the unique properties of Shape Memory Alloys to convert thermal energy into mechanical motion effectively. These actuators are compact, lightweight, and capable of generating substantial force relative to their size, making them ideal for applications where space is at a premium. With their growing popularity in fields such as robotics and aerospace engineering, SMA wire actuators are revolutionizing how we think about actuation technology.
How SMA Actuators Work
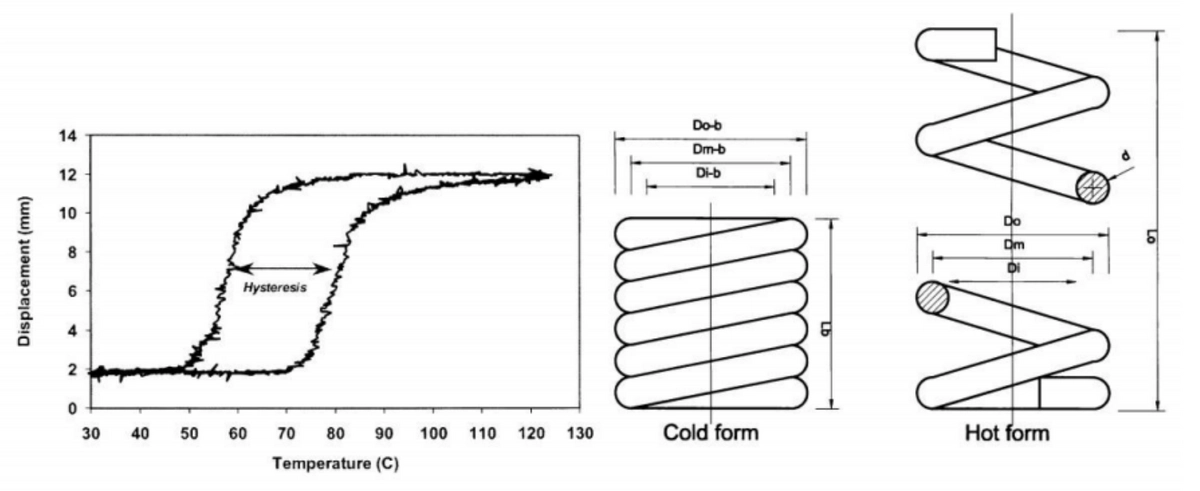
The working principle behind SMA actuators revolves around the transformation between two different crystalline phases: martensite and austenite. When an SMA actuator is heated above its transformation temperature, it transitions from martensite—a low-energy phase—to austenite—a high-energy phase—resulting in movement or actuation. This process not only highlights the ingenuity behind memory metal actuators but also illustrates why understanding the SMA actuator working principle is crucial for optimizing their performance in various applications.
What is Shape Memory Alloy?

Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) are fascinating materials that have the unique ability to return to a predetermined shape when heated above a certain temperature. This remarkable property makes them ideal for various applications, particularly in actuators. Among these, the SMA wire actuator stands out due to its efficient performance and versatility.
Overview of SMA Properties
SMA materials exhibit two primary properties: the shape memory effect and superelasticity. The shape memory effect allows an SMA actuator to remember its original form after being deformed, while superelasticity enables it to undergo significant deformation without permanent changes at specific temperature ranges. These properties make SMAs, especially Nitinol wire, highly desirable for applications requiring precise movement and reliability.
In addition to their unique mechanical properties, Shape Memory Alloys are also lightweight and corrosion-resistant, further enhancing their appeal in various engineering fields. The combination of these characteristics allows for innovative designs in robotics and medical devices where space and weight constraints are critical. Overall, the intriguing properties of SMAs provide a strong foundation for their use in advanced technologies like the SMA actuator working principle.
Types of Shape Memory Alloys
There are several types of Shape Memory Alloys available today, with Nitinol being one of the most widely used due to its excellent performance characteristics. Nitinol is an alloy composed primarily of nickel and titanium, known for its exceptional shape memory capabilities and biocompatibility—making it suitable for medical applications such as stents or surgical tools. Other types include copper-based alloys which can be more cost-effective but may not offer the same level of performance as Nitinol.
Each type has distinct advantages depending on the application; for example, some may exhibit higher transformation temperatures while others may offer better fatigue resistance. Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting an SMA actuator for specific tasks or environments. Ultimately, choosing between various types ensures that engineers harness the full potential of Shape Memory Alloy actuator applications.
The Evolution of Shape Memory Alloys
The journey of Shape Memory Alloys began in the 1930s with initial discoveries that laid the groundwork for future innovations in this field. Over decades, advancements in material science have led to enhanced understanding and manipulation of SMA properties—resulting in more reliable and efficient actuators like those made from Nitinol wire today.
In recent years, research has accelerated around improving SMA technology through better processing techniques and alloy compositions, driving down costs while increasing performance capabilities across various industries including robotics and aerospace engineering. As we look ahead, it's clear that ongoing innovations will continue shaping how we utilize SMAs—ensuring they remain at the forefront alongside other technologies like piezoelectric actuators.
The Mechanics of SMA Actuator Working Principle

Understanding the mechanics behind SMA actuators is essential for grasping their unique capabilities and applications. These devices leverage the remarkable properties of Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs), particularly Nitinol, to convert thermal energy into mechanical motion. This section delves into the operational principles that make SMA wire actuators so effective in various applications.
How SMA Wire Actuators Operate
SMA wire actuators operate on a fascinating principle: they change shape in response to temperature changes. When heated above a certain threshold, known as the transformation temperature, the Nitinol wire contracts, pulling or pushing an attached load. Conversely, when cooled, the wire returns to its original shape, allowing for precise control over movement—an elegant dance of expansion and contraction that makes SMA actuators ideal for tasks requiring fine adjustments.
The simplicity of this mechanism belies its versatility; SMA actuators can be used in various applications ranging from robotics to medical devices. Their ability to generate substantial force while remaining lightweight makes them an attractive alternative to traditional actuation methods like piezoelectric actuators. With continuous advancements in materials science, the efficiency and reliability of these memory metal actuators are only set to improve.
Heating and Cooling in SMA Actuators
Heating and cooling are critical processes that govern how effectively an SMA actuator performs its intended function. Typically, electrical resistance heating is employed to rapidly raise the temperature of Nitinol wires when activated by an electric current. This rapid thermal response enables quick actuation cycles; however, effective heat dissipation during cooling is equally important for maintaining performance and longevity.
Cooling can occur naturally through ambient air or be facilitated by external means such as fans or heat sinks for more demanding applications. The rate at which an SMA actuator cools influences its responsiveness—faster cooling allows quicker return cycles but may require additional design considerations for heat management. Thus, understanding these thermal dynamics is crucial when integrating Shape Memory Alloy actuator applications into systems where timing and precision are paramount.
The Role of Phase Transformation
At the heart of every Nitinol actuator's operation lies phase transformation—a process that underpins their unique ability to remember shapes based on temperature conditions. In its high-temperature phase (austenite), Nitinol exhibits a linear shape; when cooled below a specific point (martensite), it can deform without losing its new configuration until reheated again. This reversible transformation allows SMA wire actuators not just to move but also to retain specific positions without continuous power input.
This property opens up possibilities for energy-efficient designs where power consumption is minimized during static phases—ideal for long-term deployments like aerospace engineering or medical devices where battery life is crucial. Understanding this phase transformation mechanism helps engineers innovate further within Shape Memory Alloy actuator applications while maximizing performance across various sectors from robotics to consumer electronics.
Applications of Shape Memory Alloy Actuators

Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) have emerged as game-changers across various industries, proving their versatility and efficiency in numerous applications. The unique properties of SMA wire actuators, particularly their ability to return to a predetermined shape when heated, make them ideal for innovative solutions in robotics, aerospace engineering, and the medical field. This section will explore how SMA actuator working principles are revolutionizing these sectors.
Revolutionizing Robotics with SMA Actuators
In the realm of robotics, SMA actuators are leading the charge towards lighter and more efficient designs. Their compact size and lightweight nature allow engineers to create robotic systems that can perform complex movements without the bulk of traditional motors. For instance, SMA wire actuators can be integrated into soft robotics, enabling delicate manipulation tasks that require precision without sacrificing strength.
Moreover, the responsiveness of Nitinol actuators—another name for shape memory alloys—enables robots to adapt quickly to changing environments. This adaptability is crucial in applications like search-and-rescue missions where robots need to navigate unpredictable terrains. As researchers continue to explore new configurations and designs using memory metal actuators, we can expect even more groundbreaking advancements in robotic capabilities.
Use Cases in Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineering has also benefited significantly from the integration of SMA technology. The lightweight yet robust characteristics of shape memory alloy actuators make them suitable for various applications within aircraft systems. For example, they can be employed in adaptive wing structures that change shape during flight for improved aerodynamics and fuel efficiency.
Additionally, SMAs have been utilized in deployable structures such as antennas or solar panels on spacecraft where space is at a premium. The ability of Nitinol wire to undergo phase transformations allows these components to fold neatly during launch and expand once they reach their destination—providing functionality without added weight or complexity. As aerospace technologies evolve, the demand for innovative solutions like SMA actuators will likely continue to rise.
Medical Applications of Nitinol Actuators
The medical field has seen remarkable advancements through the use of Nitinol actuators due to their biocompatibility and flexibility. One prominent application is in stents—tiny mesh tubes used to keep blood vessels open—where SMA technology enables them to expand upon reaching body temperature after being inserted in a compressed state. This feature not only enhances patient outcomes but also reduces recovery times.
Furthermore, memory metal actuators are making waves in surgical tools designed for minimally invasive procedures where precision is key. By harnessing the unique properties of SMAs, surgeons can manipulate instruments with greater control while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues during operations. With ongoing research into new medical applications for shape memory alloys, we anticipate even more transformative uses on the horizon.
Comparing SMA Actuators and Piezoelectric Actuators

When it comes to actuators, the battle between SMA wire actuators and piezoelectric actuators is quite intriguing. Both technologies offer unique advantages and applications, but their operating principles differ significantly. Understanding these differences can help engineers choose the right actuator for their specific needs.
Key Differences Between SMA and Piezoelectric Actuators
The primary distinction between SMA actuators and piezoelectric actuators lies in their operational mechanisms. The SMA actuator relies on phase transformation in materials like Nitinol to convert thermal energy into mechanical movement, while a piezoelectric actuator utilizes electric fields to induce deformation in certain materials. This fundamental difference leads to variations in response times, force outputs, and energy consumption profiles.
Another notable difference is the range of motion each actuator can achieve; SMA wire actuators often provide larger displacements compared to the more limited movement of piezoelectric devices. Additionally, while piezoelectric actuators are known for their precision and rapid response times, they typically require a continuous power supply to maintain their position—whereas an SMA actuator can hold its shape without ongoing energy input once activated. Understanding these key differences is vital when selecting the appropriate technology for your project.
Advantages of SMA Wire Actuators
SMA wire actuators boast several advantages that make them appealing for various applications. One significant benefit is their ability to generate large forces relative to their size, which allows for compact designs without sacrificing performance—ideal for robotics and aerospace engineering where space is at a premium. Furthermore, Nitinol’s unique properties enable these memory metal actuators to operate silently, making them suitable for environments where noise reduction is critical.
Another advantage lies in the simplicity of control; SMA actuators only require heat application or removal to function effectively, reducing the complexity associated with electrical systems found in piezoelectric devices. This straightforward operation translates into lower costs regarding both manufacturing and maintenance over time. With fewer moving parts involved in an SMA actuator's working principle compared to its piezoelectric counterpart, there’s also less risk of mechanical failure—a win-win situation!
Ideal Scenarios for Each Technology
Choosing between an SMA wire actuator and a piezoelectric actuator often depends on specific project requirements or constraints. For applications requiring high force output with substantial displacement—such as robotic arms or prosthetics—the shape memory alloy actuator shines due to its impressive strength-to-weight ratio and efficient thermal response characteristics. Conversely, if your project demands precise positioning with rapid actuation speeds—think optical devices or micro-manipulation tasks—a piezoelectric actuator would be more suitable given its fine control capabilities.
In summary, both technologies have their rightful place within modern engineering contexts; understanding when each excels will ensure you achieve optimal results in your designs! Whether it’s leveraging Nitinol's innovative properties through an SMA actuator or harnessing electrical precision via a piezoelectric device, knowing your options paves the way for success.
The Future of Nitinol Wire and Memory Metal Actuators

The future of Nitinol wire and memory metal actuators is brimming with potential as advancements in technology continue to unfold. With the increasing demand for efficient and compact actuation solutions, SMA wire actuators are poised to take center stage across various industries. As we delve into the innovations, market trends, and key players like GEE SMA, it becomes clear that the evolution of SMA actuators is just beginning.
Innovations in SMA Technology
Recent innovations in SMA technology have led to significant improvements in performance and versatility. Researchers are developing new alloys and processing techniques that enhance the responsiveness of shape memory alloy actuators, allowing for faster actuation times and greater energy efficiency. Additionally, integration with smart materials has opened doors to advanced applications where Nitinol actuators can be controlled with precision, adapting dynamically to changing conditions.
These breakthroughs not only expand the capabilities of SMA actuators but also make them more appealing compared to traditional actuation methods like piezoelectric actuators. For instance, enhanced fatigue resistance in newer SMA wire designs means longer lifespans and reduced maintenance costs for applications ranging from robotics to aerospace engineering. As these innovations continue to emerge, the versatility of shape memory alloy actuator applications will undoubtedly grow.
Potential Market Growth and Trends
The market for Nitinol wire and memory metal actuator technologies is on a trajectory toward exponential growth as industries increasingly recognize their advantages over conventional systems. Analysts predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) that reflects rising investments in sectors such as automotive, healthcare, and robotics—where lightweight components are crucial for efficiency. This trend is particularly pronounced in medical applications where Nitinol actuators offer minimally invasive solutions that improve patient outcomes.
Moreover, sustainability concerns are driving manufacturers towards eco-friendly alternatives like shape memory alloys that require less energy during operation compared to piezoelectric actuators or other traditional systems. As industries strive for greener technologies, the demand for innovative SMA actuator solutions will likely surge even further—making it an exciting time for developers and manufacturers alike.
GEE SMA's Role in Advancing SMA Technology
GEE SMA has emerged as a pivotal player in advancing SMA technology by focusing on quality control and innovation within their product lines. Their dedication to research has led them to develop cutting-edge Nitinol wire products that push the boundaries of what shape memory alloy actuators can achieve today. By investing heavily in R&D initiatives aimed at refining the performance characteristics of their SMAs, GEE SMA ensures they remain at the forefront of this rapidly evolving field.
In addition to product development, GEE SMA actively collaborates with various industries to tailor their shape memory alloy actuator applications according to specific needs—whether it's enhancing robotic movement or improving medical devices' functionality. Their commitment not only fosters innovation but also positions them as trusted partners within diverse markets looking for reliable solutions using advanced materials like Nitinol wire.
In conclusion, as we move forward into an era characterized by rapid technological evolution, both innovations in SMA technology and strategic partnerships will play crucial roles in shaping the future landscape of actuator solutions worldwide.
Conclusion
In a world where innovation drives progress, SMA actuators stand out as a game-changing technology in various fields. Their unique ability to change shape and exert force through temperature variations makes them incredibly versatile, offering solutions that traditional actuators simply cannot match. With applications spanning robotics, aerospace, and medicine, the choice to adopt SMA wire actuators is clear for engineers and designers seeking efficiency and reliability.
Why Choose SMA Actuators?
Choosing SMA actuators means opting for a technology that combines efficiency with compactness. Unlike traditional piezoelectric actuators that require complex circuitry and can be bulky, the sleek design of an SMA actuator allows for integration into tight spaces without sacrificing performance. Moreover, the SMA actuator working principle—relying on phase transformation—enables it to provide significant force output with minimal energy consumption, making it an eco-friendly choice.
The durability of Nitinol wire also adds to its appeal; these memory metal actuators can endure countless cycles without losing functionality. This longevity translates into lower maintenance costs over time, further solidifying the case for incorporating Shape Memory Alloy actuator applications into engineering projects. In essence, choosing SMA wire actuators equates to investing in a reliable future where performance meets sustainability.
The Impact of Nitinol on Modern Engineering
Nitinol has revolutionized modern engineering by introducing new possibilities in design and functionality across multiple sectors. Its unique properties allow for innovative approaches in creating devices that are not only efficient but also lightweight and compact—a crucial factor in industries like aerospace where every gram counts. The ability of Nitinol actuators to undergo significant shape changes under varying temperatures has opened doors to designs previously thought impossible.
Furthermore, the integration of Shape Memory Alloy actuator applications into medical devices exemplifies how Nitinol is reshaping healthcare technology. From stents that adapt within the body to minimally invasive surgical tools that respond dynamically during procedures, Nitinol’s versatility enhances patient outcomes significantly. As engineers continue to explore its potential, we can anticipate even more groundbreaking developments in various fields thanks to this remarkable memory metal actuator.
GEE SMA’s Commitment to Quality and Innovation
At GEE SMA, our commitment lies not just in providing high-quality Nitinol wire but also in pushing the boundaries of what is possible with SMA technology. We understand that each application has unique requirements; hence we focus on continuous innovation tailored specifically for our clients’ needs. By investing heavily in research and development, GEE SMA is at the forefront of advancements in shape memory alloys.
Our dedication extends beyond just product offerings; we aim to educate our partners about the advantages of using sma wire actuators versus other technologies like piezoelectric actuators through workshops and seminars. This holistic approach ensures that clients are well-informed about their options while benefiting from our state-of-the-art solutions designed for superior performance and reliability. Together with our partners, we are shaping a future where Nitinol-based technologies lead the way toward smarter engineering solutions.

