Introduction
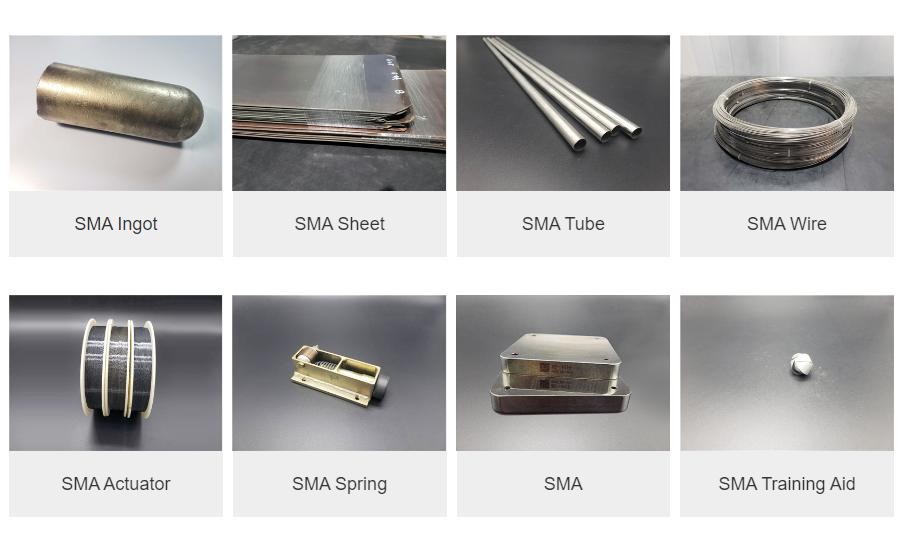

Shape memory alloys (SMAs) are fascinating materials that can remember their original shape after being deformed. This unique property makes them invaluable in various applications, from medical devices to aerospace technology. By understanding the structure of shape memory alloys and their properties, we can appreciate why these materials are at the forefront of innovation.
Understanding Shape Memory Alloys
At their core, shape memory alloys are metallic materials that exhibit a remarkable ability to return to a predetermined shape when subjected to specific temperature changes. The structure of shape memory alloys typically consists of two phases: a high-temperature phase and a low-temperature phase, which allows them to switch between shapes effectively. This intriguing behavior is largely due to the unique arrangement of atoms within the alloy, which enables it to undergo reversible transformations.
Why Shape Memory Alloys Matter
The significance of shape memory alloys cannot be overstated; they offer solutions that traditional materials simply cannot provide. For instance, their ability to recover from deformation opens up new possibilities in design and engineering, making them ideal for applications where flexibility and resilience are paramount. Furthermore, as industries increasingly seek innovative solutions, understanding the price trends of shape memory alloys becomes essential for investment decisions and technological advancements.
Real-World Applications of Shape Memory Alloys
Shape memory alloys find diverse uses across multiple sectors due to their extraordinary properties. In the medical field, they are utilized in stents and guidewires that adapt seamlessly within the human body, improving patient outcomes significantly. Additionally, industries such as automotive and aerospace leverage these materials for components that require both strength and adaptability; for example, Shape Memory Alloys Armored Core systems enhance performance while minimizing weight.
The Science Behind Shape Memory Alloys
When diving into the world of shape memory alloys, one quickly realizes that these materials are not just simple metals; they possess extraordinary capabilities. With unique properties that allow them to return to a predetermined shape when heated, shape memory alloys are a fascinating blend of science and engineering. Their ability to 'remember' shapes makes them invaluable in various applications, from medical devices to aerospace innovations.
Properties of Shape Memory Alloys
The properties of shape memory alloys are what set them apart from conventional materials. These alloys exhibit two main phenomena: the shape memory effect and superelasticity. The former allows them to revert to a specific shape upon heating, while the latter enables them to undergo significant deformation and return to their original form when stress is removed—both critical features for many shape memory alloys uses.
In addition to these remarkable behaviors, the temperature sensitivity of these materials is another key property. Each alloy has a specific transformation temperature range where these effects take place, making it essential for engineers and designers to understand these nuances for effective application in products like the Shape Memory Alloys Armored Core. Furthermore, their corrosion resistance and fatigue durability enhance their viability in demanding environments.
Structure of Shape Memory Alloys
The structure of shape memory alloys plays a pivotal role in their functionality. Typically composed of metallic elements such as nickel and titanium (as seen in Nitinol), these alloys have a distinct crystalline structure that changes with temperature variations. This transformation between different phases—usually from martensite at lower temperatures to austenite at higher temperatures—is crucial for enabling the unique properties associated with shape memory alloys.
The arrangement of atoms within these phases is what allows for such impressive mechanical behavior; it's like having an entire team that knows how to switch positions seamlessly! Understanding this structural dynamic not only informs researchers about potential new alloy combinations but also aids in refining existing ones for better performance across various applications.
How Shape Memory Alloys Work
So how do shape memory alloys work? Essentially, when an alloy is deformed at lower temperatures (in its martensitic phase), it can be reshaped without permanent alteration—pretty cool, right? When heated above its transformation temperature, the material undergoes a phase change back into its original form (austenitic phase), effectively 'remembering' its predefined structure.
This process is not just magic; it’s rooted deeply in thermodynamics and crystallography principles! For instance, applying stress while the material is still cold will allow it to hold onto its new form until heat triggers its return journey—a phenomenon exploited across numerous industries today. Whether it's used in stents or actuators within robotics (think about those nifty devices powered by innovative shape memory alloys examples), understanding how they work opens up new avenues for technological advancements.
Popular Shape Memory Alloys Examples

Shape memory alloys (SMAs) have gained significant attention due to their unique properties and versatile applications. Among the various shape memory alloys examples, Nitinol stands out for its remarkable capabilities in robotics, while brass and copper-based SMAs offer intriguing alternatives in different fields. Understanding these materials' structure and properties helps us appreciate their diverse uses.
Nitinol in Robotics
Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy, is one of the most well-known shape memory alloys due to its exceptional properties that make it ideal for robotics applications. Its ability to return to a predetermined shape when heated allows engineers to create innovative actuators and joints that mimic natural movements. The integration of Nitinol into robotic systems not only enhances flexibility but also reduces weight, making robots more efficient and agile.
Moreover, the use of Nitinol in robotics demonstrates the potential of shape memory alloys to revolutionize how machines interact with their environment. For instance, robotic grippers made from Nitinol can adapt their grip strength based on the object being handled, showcasing a level of sophistication previously unattainable with traditional materials. As research continues into optimizing these shape memory alloys properties, we can expect even more groundbreaking advancements in robotic technology.
Brass Shape Memory Alloys Applications
Brass shape memory alloys are lesser-known but equally fascinating examples of SMAs with unique advantages across various applications. These alloys exhibit a lower transformation temperature than many other SMAs, making them suitable for specific uses where heat sensitivity is crucial. Their excellent ductility and corrosion resistance further enhance their appeal in industries such as telecommunications and consumer electronics.
One notable application of brass SMAs lies in the manufacturing of connectors and switches that respond dynamically to changes in temperature or mechanical stress. By incorporating these smart materials into devices, manufacturers can create more reliable products that enhance user experience through improved performance and longevity. As companies continue exploring brass shape memory alloys uses, we may see an increasing trend toward smart technologies driven by these innovative materials.
Copper-Based Shape Memory Alloys
Copper-based shape memory alloys are another exciting category within the SMA family known for their distinct characteristics and advantages over traditional options like Nitinol or brass SMAs. These materials typically boast higher thermal conductivity and better fatigue resistance compared to other SMAs, making them particularly appealing for applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. The structure of shape memory alloys plays an essential role here; copper-based variants often exhibit enhanced mechanical properties due to their crystalline arrangements.
In practical terms, copper-based SMAs find utility in various sectors such as aerospace engineering and automotive manufacturing where robust performance is essential under fluctuating temperatures or loads. Their ability to undergo significant deformation while still returning to their original form opens up new possibilities for innovative designs that prioritize both functionality and safety. With ongoing advancements focused on refining copper-based shape memory alloys price points through improved production techniques, we may witness broader adoption across multiple industries soon.
Shape Memory Alloys Uses in Industries

Shape memory alloys (SMAs) have carved out a niche across various industries due to their unique properties and versatile applications. From medical devices that save lives to aerospace innovations that push the boundaries of technology, shape memory alloys are transforming how we think about materials and their potential uses. This section delves into the specific applications of shape memory alloys, illustrating their impact on multiple sectors.
Medical Devices Utilizing Shape Memory Alloys
In the medical field, shape memory alloys are revolutionizing device design and functionality. One prominent example is Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy known for its remarkable shape memory properties and biocompatibility. It’s used in stents, guidewires, and surgical tools, allowing for minimally invasive procedures that enhance patient recovery times.
The unique structure of shape memory alloys enables them to return to a predetermined shape when heated, making them ideal for applications where flexibility is crucial. For instance, during surgery, Nitinol can be inserted into the body in a compact form but expands once it reaches body temperature. This characteristic not only improves the efficacy of medical devices but also provides patients with safer treatment options.
Moreover, as advancements continue in SMA technology, we can expect even more innovative uses within healthcare. The ongoing research into new shape memory alloys examples promises improvements in durability and functionality for devices like orthopedic implants or dental braces. As these materials evolve, their price may fluctuate; however, their value in enhancing medical outcomes remains undeniable.
Aerospace Applications of Shape Memory Alloys
The aerospace industry has embraced shape memory alloys due to their lightweight nature and exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. SMAs are being utilized in adaptive structures such as wings and control surfaces that can change shapes based on flight conditions—an innovation inspired by nature's own design principles! The ability to manipulate these structures dynamically enhances aircraft performance while optimizing fuel efficiency.
One standout application involves using SMAs for actuators that control aerodynamic surfaces on aircraft wings or rotor blades. These smart materials respond quickly to environmental changes without needing heavy mechanical systems—making them an attractive alternative for modern aerospace engineering challenges. Their impressive properties contribute significantly to reducing overall aircraft weight while maintaining structural integrity during flight.
Additionally, as space exploration continues to advance with missions aimed at Mars or beyond, SMAs play a critical role in deploying solar panels or antennas on spacecrafts through mechanisms like the Shape Memory Alloys Armored Core technology. This innovative approach allows spacecraft components to unfold seamlessly once they reach space temperatures—a feat not easily achievable with traditional materials alone.
Automotive Industry and Shape Memory Alloys
In the automotive sector, shape memory alloys are driving innovations that enhance safety features and improve vehicle performance. From self-healing components to adaptive seating systems that adjust based on passenger weight or posture—SMAs are paving the way for smarter cars equipped with responsive technologies! The unique properties of these materials allow them to change shapes under specific conditions without compromising strength or durability.
One exciting application is found in active suspension systems where SMAs help maintain optimal ride comfort by adjusting stiffness based on road conditions automatically. This adaptability not only enhances driving experience but also contributes significantly towards improved fuel efficiency by optimizing vehicle dynamics continuously throughout operation.
Moreover, as manufacturers seek ways to reduce production costs while maintaining high-quality standards—investments into developing cost-effective SMA solutions become increasingly appealing! With ongoing research focusing on new alloy compositions and processing techniques aimed at lowering the price of these advanced materials—we can anticipate even broader adoption across various automotive applications soon!
GEE SMA and Nitinol Innovations

As the demand for advanced materials continues to rise, GEE SMA is at the forefront of innovations in shape memory alloys, particularly with Nitinol. These materials are not just a scientific curiosity; they play a pivotal role in various cutting-edge applications, especially in space missions. By leveraging the unique properties of shape memory alloys, GEE SMA has developed solutions that enhance performance and reliability in extreme environments.
GEE SMA's Role in Space Missions
In space exploration, every component must withstand harsh conditions while maintaining functionality—this is where shape memory alloys shine. GEE SMA has integrated Nitinol into several critical systems used in spacecraft, from deployable structures to actuators that respond dynamically to environmental changes. The ability of these shape memory alloys to revert to predefined shapes under specific temperatures makes them ideal for applications such as antenna deployment and solar panel orientation.
The structure of shape memory alloys allows them to endure significant stress without permanent deformation, making them perfect for the unpredictable nature of space travel. For instance, when subjected to extreme temperature fluctuations during launch or re-entry, Nitinol components can perform consistently without failure. This reliability not only enhances mission success rates but also contributes significantly to reducing costs associated with repairs or replacements.
Tailored Solutions from GEE SMA
GEE SMA excels at providing tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of various industries utilizing shape memory alloys. Their expertise allows them to customize properties such as transformation temperatures and mechanical characteristics based on specific application requirements. This level of customization ensures that clients receive optimal performance from their products while maximizing efficiency and safety.
For example, when developing components for medical devices or aerospace applications, GEE SMA can modify the structure of shape memory alloys to achieve desired responses under different conditions. This adaptability makes their offerings versatile across multiple sectors—from robotics using Nitinol actuators to automotive parts designed with brass-based shape memory alloys examples. The result is a suite of innovative solutions that push the boundaries of what’s possible with traditional materials.
Quality Assurance in Shape Memory Alloys Production
Quality assurance is paramount when it comes to producing reliable shape memory alloys; after all, even minor defects can lead to catastrophic failures in critical applications like aerospace or medical devices. At GEE SMA, rigorous testing protocols are implemented throughout the production process of their shape memory alloys products—ensuring consistency and performance under varied conditions. This meticulous attention guarantees that each batch meets strict industry standards before it ever reaches customers.
Furthermore, employing advanced manufacturing techniques helps maintain high-quality control over every aspect—from raw material selection through final processing stages—resulting in superior products like those found within Shape Memory Alloys Armored Core systems used by defense contractors worldwide. As a result, clients can trust that they are investing not just in innovative technology but also in reliable performance backed by comprehensive quality assurance measures.
In conclusion, whether through pioneering advancements for space missions or offering tailored solutions across industries utilizing various types of shape memory alloys—including brass and copper-based variants—GEE SMA stands out as a leader committed to excellence and innovation within this exciting field.
The Economics of Shape Memory Alloys
The economics surrounding shape memory alloys (SMAs) is a fascinating intersection of innovation, market demand, and production costs. As industries increasingly adopt these materials for their unique properties, understanding price trends becomes essential for businesses and consumers alike. With the rise in applications across various sectors, the economic landscape of shape memory alloys is evolving rapidly.
Shape Memory Alloys Price Trends
The price trends of shape memory alloys have shown significant fluctuations over the past decade, influenced by factors such as raw material availability and technological advancements. Initially considered expensive due to their complex production processes, prices have gradually stabilized as manufacturing techniques improve and competition increases within the market. Furthermore, with growing demand in sectors like aerospace and medical devices—where specific shape memory alloys examples are frequently utilized—prices may continue to reflect this upward trend influenced by supply chain dynamics.
Cost-Effectiveness of Shape Memory Alloys
When evaluating cost-effectiveness, shape memory alloys stand out due to their ability to perform multiple functions within a single material. For instance, in applications like robotics or automotive systems where durability is crucial, the long lifespan and reliability offered by SMAs can lead to substantial savings over time. Additionally, the lightweight nature and adaptability of these materials mean that they can enhance overall product efficiency while reducing energy consumption—an essential consideration for manufacturers seeking sustainable solutions.
Investment in Shape Memory Alloys Technology
Investment in shape memory alloys technology is on an upward trajectory as industries recognize their transformative potential across various applications. Companies are channeling funds into research and development to unlock new functionalities and improve existing structures of shape memory alloys, ensuring they remain competitive in an ever-evolving marketplace. As more innovations emerge—like those seen with Shape Memory Alloys Armored Core—the long-term benefits of investing in SMA technology are becoming increasingly apparent.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of shape memory alloys, it's clear that these materials are not just a scientific curiosity but a cornerstone of modern technology. The future trends in shape memory alloys suggest that we will see even more innovative applications, driven by ongoing research and development in their properties and structures. As industries continue to recognize the unique advantages of shape memory alloys, their adoption is likely to expand into new sectors and applications.
Future Trends in Shape Memory Alloys
Looking ahead, the future trends in shape memory alloys point toward enhanced functionality and versatility. Researchers are focusing on improving the structure of shape memory alloys to create even more responsive materials that can adapt to varying conditions. Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing techniques may lead to reduced costs, making these remarkable materials more accessible across various industries.
Advancements in Shape Memory Alloys Applications
In terms of advancements, the applications of shape memory alloys are evolving rapidly. From robotics to aerospace engineering, innovative uses are emerging that leverage the unique properties of these materials for greater efficiency and performance. For instance, recent developments have showcased how shape memory alloys can revolutionize medical devices, leading to less invasive procedures and improved patient outcomes.
The Continued Importance of Shape Memory Alloys
The continued importance of shape memory alloys cannot be overstated; they represent a fusion of science and practicality that drives innovation across multiple fields. As we delve deeper into their uses—from automotive systems to cutting-edge technologies like the Shape Memory Alloys Armored Core—it's evident that these materials will play a pivotal role in shaping our technological landscape. With ongoing investments fueling research into their price dynamics and cost-effectiveness, the future looks bright for shape memory alloys as key players in industrial advancement.

