Introduction

In the realm of materials science, few innovations have captured the imagination quite like shape memory alloys (SMAs). These remarkable materials possess the unique ability to return to a predetermined shape when subjected to specific temperature changes, making them invaluable in various engineering fields. Among these, nickel material—particularly in the form of Nitinol—has emerged as a frontrunner, driving advancements across multiple industries.
What is Shape Memory Alloy
Shape memory alloys are metallic materials that undergo a reversible phase transformation, allowing them to remember their original shapes after deformation. The most well-known examples include nickel-titanium alloys, commonly referred to as Nitinol, which exhibit extraordinary flexibility and strength. This property stems from their unique crystalline structure that enables shape metal to adapt and revert under different thermal conditions.
Significance in Modern Engineering
The significance of shape memory metals extends beyond mere novelty; they are transforming how engineers approach design challenges across various sectors. From medical devices that improve patient outcomes to automotive innovations enhancing safety and efficiency, SMAs are changing the game. Their ability to operate reliably under extreme conditions makes them essential for modern engineering solutions.
Overview of Innovative Applications
The applications of shape memory alloys are as diverse as they are innovative, spanning fields such as medicine, aerospace, robotics, automotive technology, and consumer electronics. In healthcare, Nitinol stents have revolutionized cardiology by providing flexible yet strong support for blood vessels. Meanwhile, in aerospace and robotics, these materials enable sophisticated mechanisms that respond dynamically to environmental changes or user interactions—showcasing just how far we can push the boundaries with shape metal technology.
Medical Devices

The realm of medical devices has been significantly transformed by the advent of shape memory alloys, particularly through the use of nickel materials like Nitinol. These unique metals have properties that allow them to return to a predetermined shape when subjected to specific temperatures, making them ideal for various applications in healthcare. With their remarkable flexibility and strength, shape memory metals are paving the way for innovative solutions that enhance patient outcomes and streamline surgical procedures.
Nitinol Stents Revolutionizing Cardiology
Nitinol stents are at the forefront of cardiology advancements, offering a revolutionary approach to treating blocked arteries. The inherent properties of shape memory alloys allow these stents to expand upon reaching body temperature, ensuring they fit snugly within the vessel walls without causing damage or discomfort. This adaptability not only improves blood flow but also reduces complications associated with traditional stent designs, making Nitinol a game-changer in cardiovascular treatments.
Surgical Instruments with Shape Memory Metals
Surgical instruments crafted from shape memory metals bring precision and efficiency to operating rooms worldwide. These tools can be designed to change shape or stiffness in response to temperature changes, allowing surgeons greater control during delicate procedures. From retractors that adjust their tension automatically to clamps that adapt their grip based on tissue thickness, surgical instruments made from nickel material are enhancing surgical techniques and patient safety.
Orthopedic Implants Utilizing Shape Memory Alloys
Orthopedic implants incorporating shape memory alloys are revolutionizing how we approach bone repair and joint replacement surgeries. The unique ability of these materials to respond dynamically to body heat means they can provide optimal support as healing progresses, adapting their form as necessary throughout recovery stages. By utilizing shape metal technology in implants, patients experience improved comfort and functionality while minimizing the risk of complications typically associated with rigid implants.
Aerospace Applications
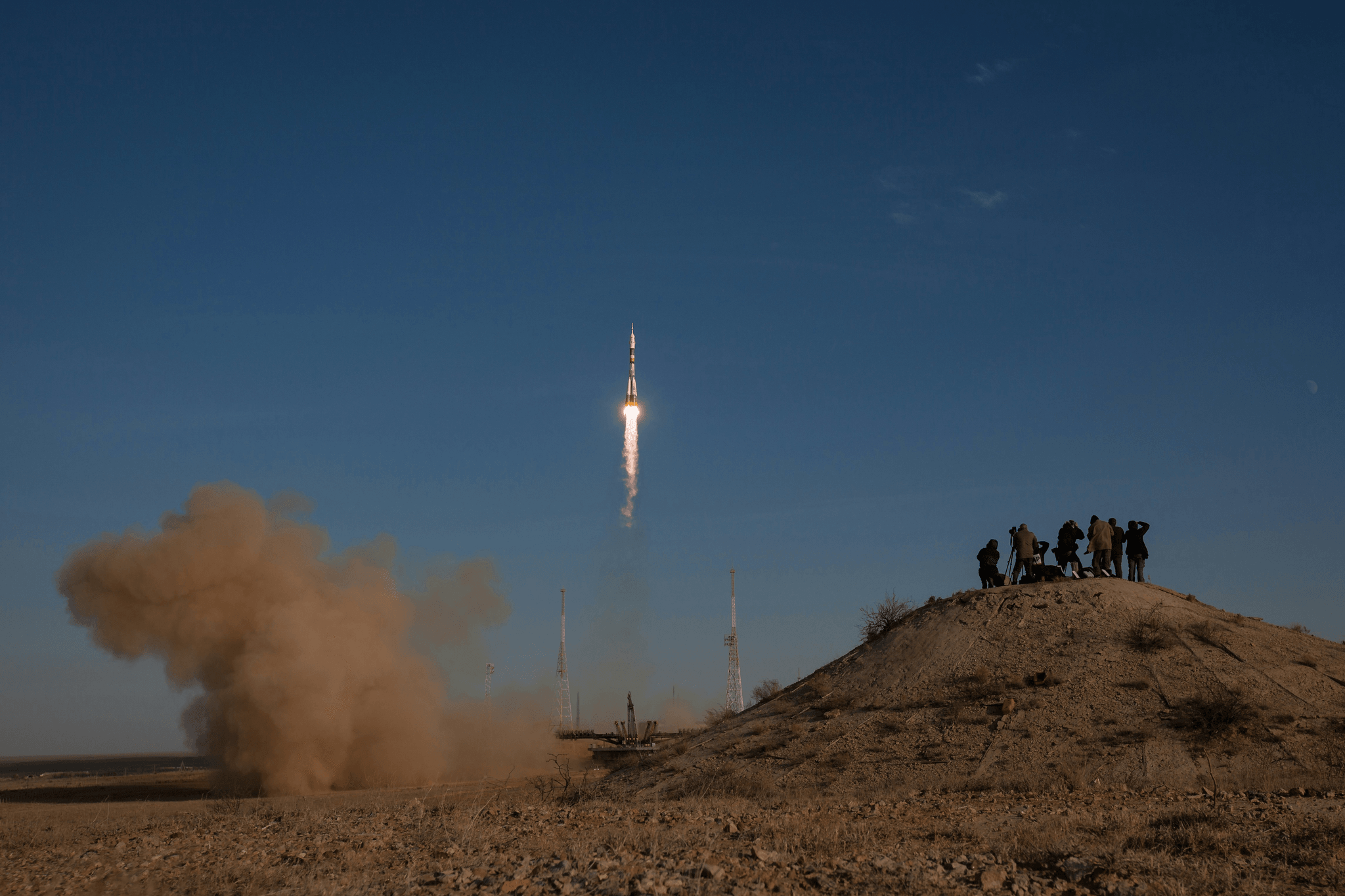
The aerospace industry is a realm where innovation meets extreme conditions, and shape memory alloys (SMAs) are leading the charge with their remarkable properties. These materials, particularly those based on nickel, have unique capabilities that allow them to return to a predetermined shape when heated. Their lightweight nature and excellent strength-to-weight ratio make them ideal candidates for various applications in space missions.
GEE SMA’s Role in Space Missions
GEE SMA has emerged as a front-runner in the development of advanced shape memory alloys for aerospace applications. By leveraging the unique properties of nickel-based shape metal, GEE SMA has created components that can adapt dynamically during space missions. This adaptability is crucial for ensuring the success of intricate operations such as satellite deployment and spacecraft assembly in zero-gravity environments.
In particular, GEE SMA's innovations include deployable structures that unfold seamlessly once they reach orbit, minimizing mechanical complexity and enhancing reliability. The ability to utilize shape memory metals allows engineers to design lighter systems without sacrificing performance or safety. As a result, GEE SMA is helping pave the way for more efficient and effective space exploration.
Shape Memory Alloys in Satellite Deployments
Shape memory alloys are revolutionizing how satellites are deployed into orbit by providing mechanisms that simplify complex processes. For instance, SMAs can be integrated into deployment systems where they act as actuators to release solar panels or antennas once the satellite reaches its designated position in space. This ensures that critical components are deployed correctly without requiring extensive mechanical systems.
The use of nickel-based shape memory metals not only reduces weight but also enhances reliability during launches and deployments—two critical factors in aerospace engineering. These materials can endure extreme temperatures and pressures while maintaining their functionality, which is essential for successful satellite operations over long periods. Consequently, SMAs are becoming indispensable tools for modern satellite technology.
Reliability in Harsh Environments
One of the standout features of shape memory alloys is their exceptional reliability when exposed to harsh environmental conditions typical of outer space. The resilience of these materials allows them to withstand severe thermal fluctuations without losing their functional integrity—a common challenge faced by many aerospace components made from traditional materials.
This durability stems from the unique properties of nickel-based shape memory metals, which retain their strength even when subjected to intense stressors like radiation or vacuum conditions found beyond Earth's atmosphere. As aerospace missions become more ambitious—venturing further from our planet—the need for reliable materials like SMAs becomes increasingly paramount for mission success and longevity.
Robotics and Actuators
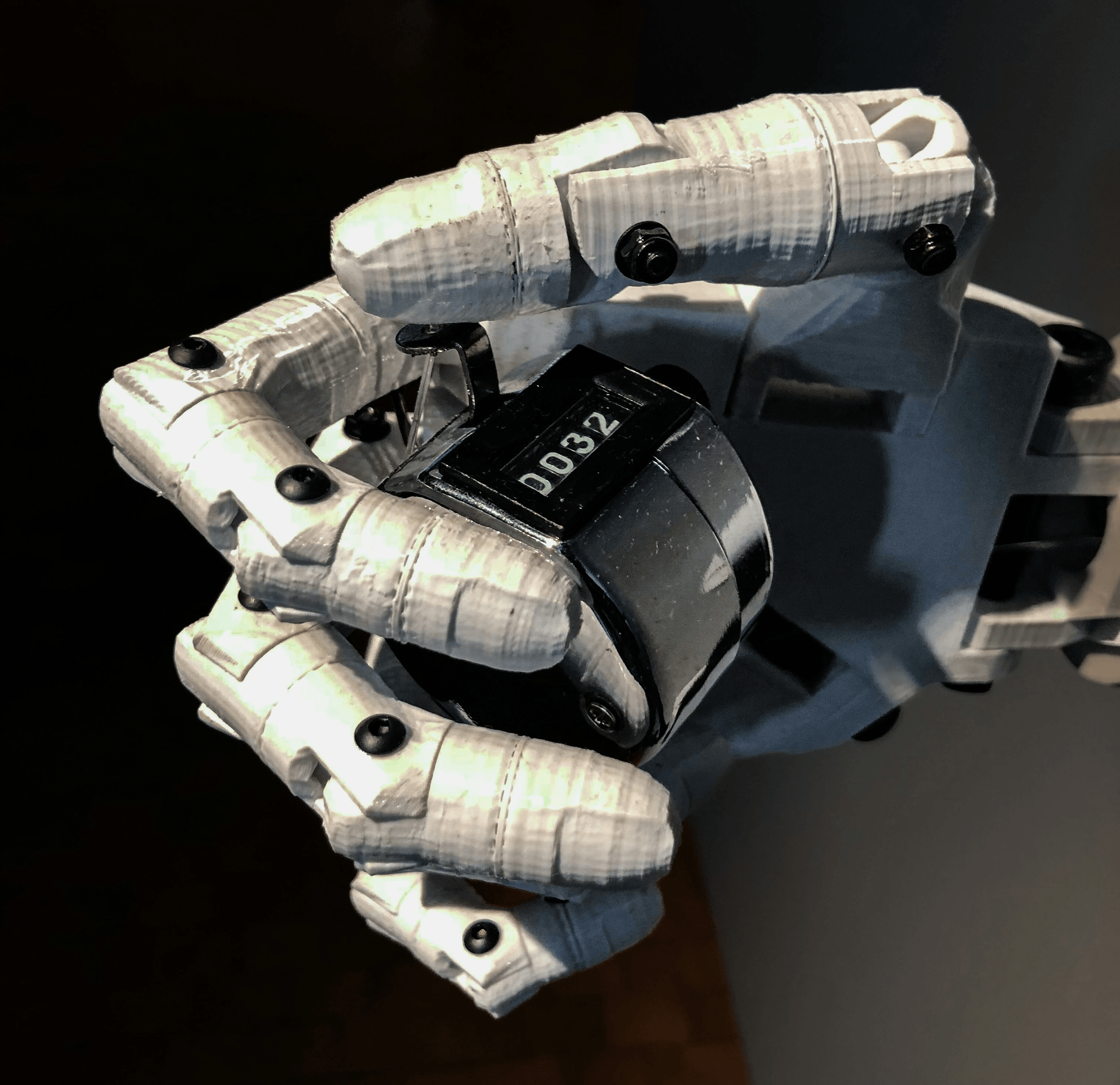
The integration of shape memory alloys (SMAs) into robotics is transforming how machines interact with their environment. These materials, particularly nickel-based shape memory metals, provide unique capabilities that enhance the functionality and adaptability of robotic systems. With their ability to change shape in response to temperature or stress, shape metals are paving the way for innovative applications in various robotic fields.
Shape Metal in Soft Robotics
Soft robotics is an exciting frontier where flexibility meets functionality, and shape metal plays a pivotal role in this evolution. By utilizing shape memory alloys, engineers can create soft actuators that mimic natural movements found in living organisms. This capability not only allows for safer interactions with humans but also enables robots to navigate complex environments with ease.
The inherent properties of SMAs allow these soft robots to respond dynamically to external stimuli, making them ideal for tasks such as delicate surgeries or intricate assembly processes. As researchers continue to explore the potential of shape metal in soft robotics, we can expect more advanced designs that blend strength with softness—truly a game changer in automation.
Adaptive Grippers with Nitinol
Nitinol, a specific type of nickel material known for its unique properties as a shape memory alloy, has revolutionized the design of adaptive grippers used in robotics. These grippers can change their form based on the object they are handling, allowing robots to grasp items ranging from fragile glassware to heavy industrial components securely. The versatility offered by Nitinol ensures that these grippers can perform efficiently across various tasks without requiring multiple specialized tools.
Moreover, the lightweight nature of Nitinol enhances the overall efficiency and speed of robotic systems while reducing energy consumption during operations. As industries increasingly demand precision and adaptability from robotic solutions, Nitinol-based grippers stand out as essential components driving innovation and performance.
Actuation Mechanisms in Robotics
Actuation mechanisms are at the heart of any robotic system's performance, and incorporating shape memory alloys brings remarkable advancements to this area. By leveraging the unique thermal properties of SMAs, engineers can design actuators that provide precise motion control while minimizing mechanical complexity. This means fewer moving parts and reduced maintenance needs—an attractive proposition for manufacturers looking to streamline their production processes.
Additionally, using nickel-based shape memory metals enhances reliability under varying environmental conditions since these materials maintain functionality even when subjected to extreme temperatures or stresses. The future looks bright for actuation mechanisms powered by SMAs as they promise not only improved efficiency but also greater resilience across diverse applications—from manufacturing lines to autonomous vehicles.
Automotive Innovations

The automotive industry is on the verge of a technological revolution, thanks to the integration of shape memory alloys (SMAs). These remarkable materials not only enhance vehicle performance but also bring innovative solutions to longstanding challenges. From self-repairing materials to advanced temperature control systems, shape memory metals are reshaping how we think about automotive design and functionality.
Self-Repairing Materials with Shape Memory Alloys
Imagine a car that can heal itself from minor dents and scratches—this is no longer a dream but a reality powered by shape memory alloys. When these materials are deformed, they can return to their original shape when subjected to heat, effectively repairing themselves without human intervention. This self-repairing capability not only enhances the longevity of vehicles but also reduces maintenance costs, making it an attractive feature for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Incorporating SMAs into vehicle exteriors means that everyday wear and tear can be mitigated with minimal effort. The use of shape memory metals in bumpers or body panels could lead to cars that maintain their pristine appearance over time. As this technology matures, we may see widespread adoption in the industry, transforming how we approach vehicle aesthetics and durability.
Temperature Control Systems using Nickel Material
Temperature regulation is critical for optimal performance in any vehicle, especially in extreme weather conditions. Nickel-based shape memory alloys play a pivotal role in developing advanced temperature control systems that adapt dynamically to changing environments. By utilizing these materials, engineers can create components that respond intelligently to thermal changes, improving both comfort and efficiency.
For example, nickel SMAs can be employed in actuators for HVAC systems within vehicles. These actuators adjust airflow based on real-time temperature readings, ensuring passengers enjoy a comfortable ride regardless of external conditions. This innovative application not only enhances user experience but also contributes to energy efficiency—an essential factor as the automotive sector moves toward sustainability.
Enhancements in Vehicle Design
The incorporation of shape metal technologies offers unparalleled flexibility in automotive design processes. With SMAs enabling unique functionalities—such as adjustable components or adaptive structures—designers are no longer limited by traditional material constraints. This freedom allows for sleeker designs that improve aerodynamics while integrating features previously deemed impractical.
Additionally, using shape memory alloys can lead to lighter vehicles without compromising strength or safety standards. As manufacturers strive for fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, lightweight construction becomes increasingly vital; SMAs provide an elegant solution by replacing heavier metal parts with more efficient alternatives made from these transformative materials. Ultimately, embracing shape memory metals could redefine what we consider possible in car design.
Consumer Electronics

In the rapidly evolving world of consumer electronics, shape memory alloys (SMAs) are carving out a niche that combines functionality with innovation. These materials, particularly those made from nickel, are not just about being trendy; they offer practical solutions that enhance user experience. From wearables to smart devices, the versatility of shape memory metals is transforming how we interact with technology.
Shape Memory Metals in Wearable Technology
Wearable technology has embraced shape memory metals like never before, integrating them into everything from fitness trackers to health monitors. The unique properties of these alloys allow devices to adapt and respond to user needs dynamically. For instance, a smartwatch could adjust its band tension based on the user's wrist size or activity level, thanks to the remarkable capabilities of shape memory alloy.
Furthermore, wearables utilizing nickel-based SMAs can provide real-time feedback by changing their form in response to environmental stimuli or user interactions. This adaptability not only enhances comfort but also opens up new avenues for functionality that were previously unimaginable. As manufacturers continue to explore these materials, we can expect even more innovative applications in personal tech.
Smart Devices with Adaptive Features
The integration of shape metal into smart devices is paving the way for a future where technology is not just static but responsive and interactive. Imagine smartphones that can change their form factor based on usage patterns—folding down when not in use or expanding when needed for gaming or viewing content! This level of adaptability is made possible through advancements in shape memory alloys.
These adaptive features aren’t limited to aesthetics; they also enhance usability and performance across various applications. For example, home automation systems equipped with SMAs can adjust shades or vents automatically based on temperature readings or sunlight exposure, optimizing energy efficiency without user intervention. With each leap forward in technology utilizing shape memory metals, our devices become more intuitive and integrated into our daily lives.
Durability and Flexibility in Electronics
Durability is a critical factor for consumer electronics, and this is where shape memory alloys shine brightly alongside traditional materials like plastics and metals. The inherent flexibility of SMAs allows them to withstand bending and twisting without compromising their structural integrity—a game changer for portable gadgets subjected to everyday wear and tear. By incorporating nickel material into electronic components, manufacturers are creating products that last longer while maintaining high performance.
Moreover, the ability of shape metal to revert back to its original form after deformation means fewer repairs and replacements over time—an appealing prospect for both consumers and manufacturers alike! As we continue embracing these innovative materials within electronics design processes, we anticipate a future filled with robust yet lightweight devices that cater seamlessly to our tech-savvy lifestyles.
Conclusion
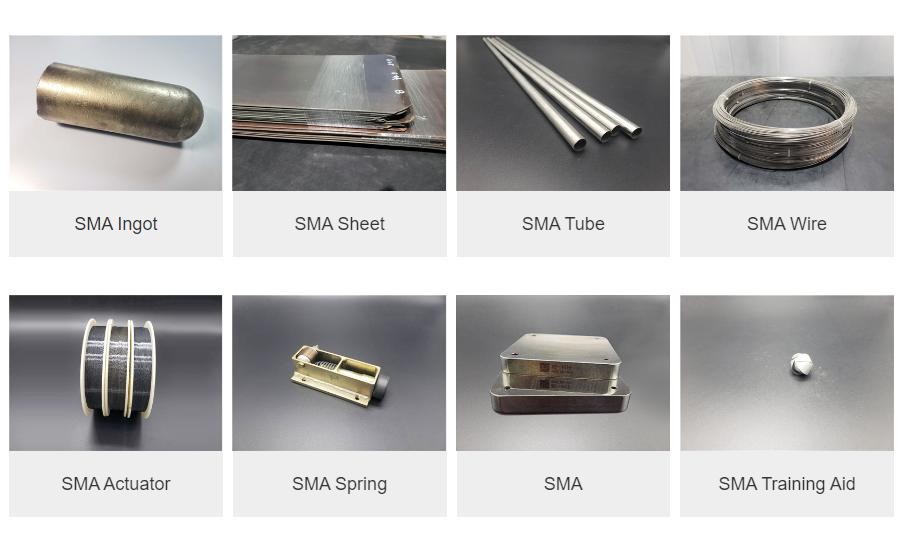

In wrapping up our exploration of shape memory alloys, it's clear that these remarkable materials are not just a passing trend; they are transforming industries across the board. From medical devices to aerospace applications, shape memory metals are redefining what is possible in engineering and design. As we advance further into the 21st century, the potential for innovation using these versatile materials appears limitless.
Transforming Industries with Shape Memory Alloys
Shape memory alloys have become essential in various sectors, proving their worth through innovative applications that enhance functionality and efficiency. In medicine, for example, Nitinol stents have revolutionized cardiology by providing flexible yet durable solutions that adapt to the body's needs. Similarly, in aerospace and automotive industries, shape metal components contribute to designs that can self-repair or adjust based on environmental conditions.
The adaptability of nickel material within these alloys allows for unprecedented levels of customization and performance. Industries are leveraging these properties to create products that not only meet but exceed current standards of safety and reliability. This transformation is a testament to how shape memory alloys can elevate operational capabilities while reducing costs and improving user experience.
The Future of Shape Memory Metals
Looking ahead, the future of shape memory metals appears bright as research continues to unveil new possibilities for their use in advanced technologies. Innovations such as smart devices equipped with adaptive features will likely become commonplace, enhancing consumer experiences across various markets. Furthermore, ongoing advancements in manufacturing techniques promise to make these materials more accessible and economically viable for widespread application.
As we explore new frontiers in robotics and automation, the role of shape metal will be crucial in developing systems that mimic natural movements with precision. The integration of these materials into everyday products will also lead to greater sustainability efforts by minimizing waste through self-healing capabilities or energy-efficient designs. Thus, the trajectory suggests an exciting evolution where shape memory alloys will play an integral role.
Why GEE SMA Leads in Nitinol Innovations
GEE SMA has positioned itself at the forefront of Nitinol innovations due to its commitment to quality and cutting-edge research methodologies focused on improving performance characteristics of shape memory alloys. Their expertise enables them to develop superior products tailored for specific applications across various industries—from medical devices that save lives to aerospace components that withstand extreme conditions.
Moreover, GEE SMA's dedication to sustainability aligns perfectly with global initiatives aimed at reducing environmental impact through advanced material science solutions like nickel material-based products designed for longevity and efficiency. Their leadership not only propels technological advancements but also sets a benchmark for others striving towards excellence within this dynamic field.
In conclusion, as we stand on the cusp of further breakthroughs involving shape memory metals, it’s evident that companies like GEE SMA are pivotal players driving this transformation forward—making our world smarter one alloy at a time.

