Introduction

In the realm of advanced materials, few innovations have sparked as much intrigue and potential as nitinol wires. These remarkable shape memory alloys, composed primarily of nickel titanium, possess unique properties that allow them to return to a predetermined shape when heated. The magic of nitinol wires lies not only in their fascinating capabilities but also in their transformative impact across various industries.
The Magic of Nitinol Wires
Nitinol wires exhibit extraordinary characteristics that set them apart from traditional materials like steel wire. When subjected to specific temperature changes, these shape memory metals can revert to their original form after being deformed, making them ideal for applications requiring flexibility and resilience. This unique behavior is a product of the alloy's intricate atomic structure, which allows it to remember its original configuration—a phenomenon that has captivated engineers and researchers alike.
A Brief History of Shape Memory Alloys
The journey of shape memory alloys began in the 1960s when researchers first discovered the unique properties of nitinol nickel titanium. Initially developed for military applications, these alloys quickly gained attention for their potential in various fields due to their remarkable performance under stress and temperature changes. Over the decades, advancements in manufacturing processes have expanded the capabilities and applications of nitinol wire, paving the way for its widespread use in medical devices and aerospace engineering.
Why Nitinol Is a Game Changer
Nitinol is undeniably a game changer in engineering solutions due to its combination of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance found in nitinol alloys. Unlike conventional materials such as steel wire, nitinol wires can undergo significant deformation while maintaining their integrity—a feature that enhances reliability in critical applications like stents or heart valves. As industries continue to explore new frontiers with metal nitinol technology, it becomes increasingly clear that this innovative material will play a pivotal role in shaping future technologies.
What Are Nitinol Wires?
Nitinol wires are a unique type of shape memory alloy that combines the elements nickel and titanium, creating a material that can return to a predetermined shape when heated. This remarkable property makes nitinol wires highly sought after in various industries, from medical devices to aerospace engineering. Understanding the composition and properties of nitinol is crucial to appreciating its transformative potential.
Composition and Properties
Nitinol is composed primarily of nickel and titanium, with varying proportions that can affect its properties. Typically, these alloys contain about 50-60% nickel and 40-50% titanium, leading to extraordinary characteristics such as flexibility, strength, and corrosion resistance. Unlike traditional steel wire, which can be rigid and prone to fatigue over time, nitinol wires exhibit remarkable resilience while maintaining their shape memory capabilities.
The unique properties of nitinol alloys stem from their crystalline structure, which can change between two phases: austenite (the high-temperature phase) and martensite (the low-temperature phase). This transformation allows for the shape memory effect; when deformed at lower temperatures (martensite), they will revert to their original form upon heating above a certain threshold (austenite). The ability of nitinol wires to remember their shapes makes them invaluable in applications where precision and reliability are critical.
The Role of Nickel Titanium
Nickel titanium plays an essential role in defining the performance characteristics of nitinol wires. The combination of these two metals creates a stable alloy that exhibits both superelasticity and shape memory effects—two attributes that set it apart from conventional materials like steel wire. This synergy allows for innovative uses in various fields where traditional materials might falter under stress or temperature changes.
Moreover, the specific ratios of nickel to titanium can be manipulated during production to tailor the mechanical properties according to application needs. For instance, increasing nickel content may enhance corrosion resistance while altering thermal behavior—a crucial factor for applications in extreme environments like space missions or medical implants. The versatility afforded by adjusting these proportions underscores why metal nitinol has become a game-changer across multiple sectors.
Understanding Shape Memory Effects
Shape memory effects are at the heart of what makes nitinol wires so fascinating and useful. When subjected to mechanical stress at lower temperatures while in the martensitic state, these alloys can be deformed significantly without permanent damage. Once heated above their transformation temperature, they remember their original shape—an effect not commonly found in most metals or even other types of shape memory metals.
This phenomenon is particularly beneficial in medical devices such as stents or heart valves that need to expand once inserted into the body but remain compact during delivery procedures. Additionally, understanding how these shape memory effects work helps engineers design more efficient systems using nitinol alloys—leading not only to improved performance but also reduced weight compared with traditional materials like steel wire. As research continues into this remarkable material's capabilities, we are likely just scratching the surface of what’s possible with nitinol wires.
Applications in Medical Devices
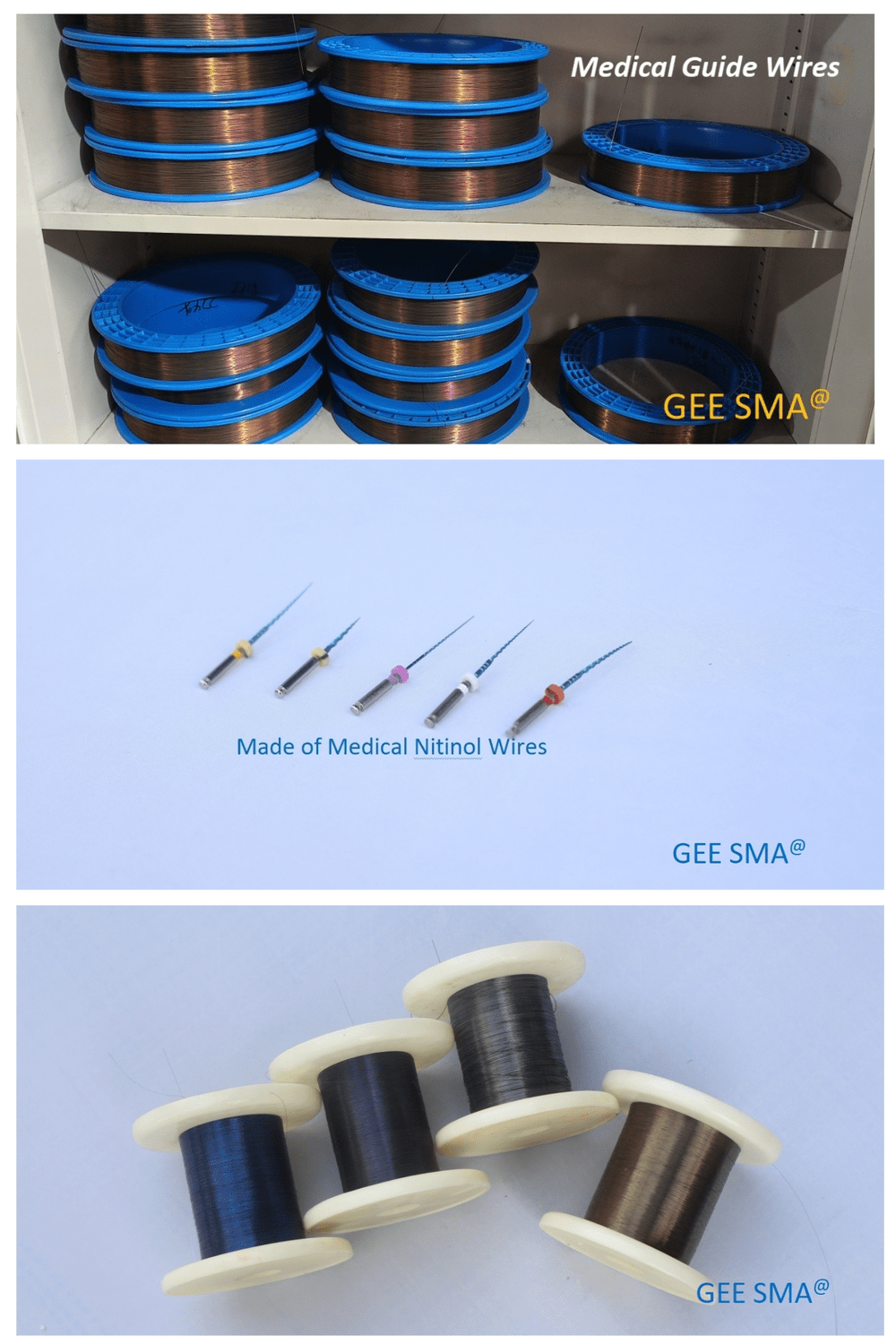

Nitinol wires have revolutionized the medical device industry, thanks to their unique properties as shape memory alloys. These remarkable materials, primarily composed of nitinol nickel titanium, offer flexibility and strength that traditional materials like steel wire simply can't match. As the demand for more effective and less invasive medical solutions grows, nitinol wires are stepping up to the challenge.
Stents and Heart Valves
When it comes to stents and heart valves, nitinol wires play a pivotal role in enhancing patient outcomes. The shape memory effect of these shape memory metals allows them to expand and contract, adapting perfectly to the body's needs during surgical procedures. This adaptability means that stents made from nitinol alloys can be delivered through small incisions and then expand within blood vessels or heart chambers, significantly reducing recovery time compared to those made from conventional materials.
Additionally, the biocompatibility of metal nitinol ensures that these devices integrate well with human tissue, minimizing complications post-surgery. Unlike steel wire alternatives that may lead to inflammation or rejection by the body, nitinol's gentle touch makes it a favorite among surgeons. With ongoing advancements in technology, we can expect even more innovative uses for these remarkable materials in cardiovascular treatments.
Minimally Invasive Surgery Tools
The rise of minimally invasive surgery has been greatly facilitated by the introduction of nitinol wires into surgical instruments. Tools crafted from this versatile alloy are not only lightweight but also exhibit superior flexibility compared to traditional options made from steel wire. This flexibility allows surgeons to navigate complex anatomical structures with ease while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
Moreover, shape memory metals like nitinol can return to their original shapes after deformation—a feature that enhances tool effectiveness during procedures such as laparoscopic surgeries or endoscopies. As a result, patients experience less pain and shorter recovery times when treated with instruments utilizing these advanced materials. The integration of nitinol wire into surgical tools is truly a game changer for modern medicine.
Biocompatibility and Reliability
One of the standout features of nitinol alloys is their exceptional biocompatibility; they are less likely than other metals to provoke adverse reactions within the human body. This reliability is crucial when considering long-term implants such as stents or orthopedic devices where patient safety is paramount. The inherent properties of metal nitinol ensure that these devices perform consistently over time without degradation or failure.
Furthermore, researchers continue exploring ways to enhance the performance characteristics of nitinol wires further—leading us into an era where medical devices not only meet but exceed patient expectations in terms of safety and efficacy. As innovations unfold across various medical fields—from orthopedics to cardiology—the impact of shape memory alloys will undoubtedly reshape healthcare practices worldwide for years to come.
Nitinol Wires in Aerospace Engineering

When it comes to aerospace engineering, the incorporation of nitinol wires has sparked a revolution in design and functionality. These shape memory alloys, primarily composed of nitinol nickel titanium, offer unique properties that traditional materials like steel wire simply cannot match. From enhancing the efficiency of space missions to ensuring reliability under extreme conditions, nitinol is proving to be an invaluable asset.
Innovations in Space Missions
Nitinol wires have ushered in a new era for innovations in space missions, enabling engineers to create lightweight yet robust components that can withstand the rigors of outer space. The ability of shape memory metals to return to their original form after deformation allows for mechanisms that can adapt and respond dynamically during flight. This adaptability is crucial for applications such as deployable structures and actuators that must perform flawlessly in the unpredictable environment of space.
GEE SMA's Contributions to Space Exploration
GEE SMA has made significant strides by integrating nitinol alloys into various aerospace projects, showcasing their versatility and reliability. Their research focuses on developing cutting-edge components that leverage the unique properties of metal nitinol, enhancing spacecraft performance while minimizing weight and maximizing efficiency. As a result, GEE SMA’s contributions are not just theoretical; they are actively shaping how we explore the cosmos.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
One of the standout features of nitinol wires is their exceptional performance under extreme conditions—whether it’s intense heat during re-entry or frigid temperatures found in deep space. Unlike traditional materials like steel wire, which can become brittle or lose integrity when exposed to drastic temperature changes, shape memory alloys maintain their functionality and strength even when faced with harsh environments. This resilience makes them ideal for critical aerospace applications where failure is not an option.
Advantages Over Traditional Materials

Nitinol wires have emerged as a revolutionary alternative to traditional materials, particularly in fields requiring high performance and reliability. Unlike steel wire, which can be rigid and prone to fatigue, nitinol offers unique properties that enhance both flexibility and strength. This combination makes nitinol alloys ideal for applications ranging from medical devices to aerospace engineering.
Flexibility and Strength
One of the standout features of nitinol wires is their remarkable flexibility coupled with impressive strength. When subjected to stress, these shape memory metals can undergo significant deformation without permanent damage, returning to their original shape once the load is removed. This property not only enhances the durability of products made from nitinol but also allows for innovative designs that would be impossible with conventional materials like steel wire.
In practical applications, this means that medical devices such as stents can expand and contract seamlessly within the body without risking breakage or malfunction. The ability of nitinol nickel titanium to adapt under various conditions ensures that it maintains its integrity even in challenging environments. Thus, engineers are increasingly turning to nitinol wire for solutions where flexibility and strength are paramount.
Corrosion Resistance of Nitinol Alloys
Corrosion resistance is another critical advantage offered by nitinol alloys over traditional materials like stainless steel or other metals. Nitinol's unique composition inherently protects it from rust and degradation when exposed to various environmental factors, including moisture and chemicals. This characteristic is especially vital in medical applications where biocompatibility is essential; using metal nitinol reduces the risk of adverse reactions within the human body.
The resilience against corrosion extends beyond healthcare; aerospace engineers benefit tremendously from this property as well since components are often subjected to harsh atmospheric conditions during flight missions. By replacing conventional materials with corrosion-resistant nitinol wires, manufacturers can ensure longevity and reliability in their products while minimizing maintenance costs over time. Ultimately, this leads to safer and more efficient operations across multiple industries.
Weight Reduction in Engineering Solutions
When it comes to weight reduction, few materials rival the advantages presented by shape memory alloys like nitinol wires. The density of nitinol allows engineers to design lighter structures without sacrificing performance or safety standards typically associated with heavier alternatives such as steel wire or aluminum alloys. This weight advantage becomes crucial in sectors like aerospace engineering where every gram counts toward fuel efficiency and payload capacity.
Furthermore, using lighter materials translates into lower energy consumption during transportation processes—whether it's an aircraft soaring through the skies or a surgical tool maneuvering within a patient's body. By integrating metal nitinol into their designs, engineers can achieve optimal performance while adhering strictly to weight constraints imposed by modern engineering challenges. As industries continue seeking innovative ways to improve efficiency, the integration of lightweight yet robust solutions like nitinol alloys will undoubtedly play a pivotal role.
Future Trends in Nitinol Technology
Nitinol technology is on the brink of a revolution, with exciting trends emerging across multiple industries. As more sectors discover the unique properties of nitinol wires, we can expect innovative applications to proliferate. From healthcare to aerospace, the versatility of nitinol alloys is set to redefine engineering norms.
Emerging Applications Across Industries
The potential applications for nitinol wires are expanding rapidly, particularly in fields like robotics and consumer electronics. For instance, shape memory alloys are being explored for use in soft robotics, where their ability to return to a predetermined shape can facilitate movement and functionality without complex actuators. Additionally, industries such as automotive are investigating how nitinol nickel titanium can enhance safety features through deployable structures that react dynamically during an accident.
In the realm of energy efficiency, researchers are looking at how metal nitinol could improve renewable energy systems. For example, integrating nitinol wire into solar panel designs could optimize their angle automatically based on sunlight exposure—maximizing energy capture without manual adjustment. The future looks bright as these emerging applications promise not only innovation but also sustainability.
Advances in Manufacturing Techniques
Manufacturing techniques for nitinol alloys are evolving alongside their applications, with advancements promising to make production more efficient and cost-effective. Traditional methods often struggled with the intricate processes required for shaping and treating these shape memory metals; however, new techniques like additive manufacturing (3D printing) are changing that narrative dramatically. With 3D printing technologies tailored for nitinol wire, it’s now possible to create complex geometries that were previously impractical or impossible using conventional steel wire.
Moreover, improvements in heat treatment processes have enhanced the performance characteristics of nitinol alloys significantly—allowing manufacturers to customize properties such as flexibility and strength while reducing waste during production. As these manufacturing advancements continue to unfold, they will likely drive down costs and increase accessibility for various industries looking to leverage the unique qualities of shape memory alloys.
The Role of Research and Development
Research and development play a crucial role in unlocking the full potential of nitinol technology across sectors. Ongoing studies aim not only at enhancing existing applications but also at discovering entirely new uses for these remarkable materials—such as investigating their behavior under different environmental conditions or exploring novel alloy compositions that could yield even better performance metrics than current options available in metal nitinol forms.
Collaborative efforts between academic institutions and industry leaders have already yielded promising results; breakthroughs from R&D initiatives have led to more reliable biocompatibility assessments for medical devices made from nitinol wires—a critical factor given their increasing prevalence in life-saving technologies like stents and heart valves. As investment flows into research focused on improving manufacturing techniques or developing next-generation materials within the realm of shape memory metals, we can anticipate a future rich with innovation driven by this remarkable alloy.
Conclusion

In conclusion, nitinol wires are not just a fascinating material; they represent a significant leap forward in engineering and technology. The unique properties of nitinol, particularly its shape memory effect and exceptional flexibility, have made it an indispensable resource across various industries. As we look to the future, the role of nitinol alloys will only continue to expand, transforming how we approach design and functionality.
Revolutionizing Engineering with Nitinol Wires
Nitinol wires have revolutionized engineering by providing solutions that traditional materials like steel wire simply can't match. Their combination of strength and flexibility allows for innovative designs that can adapt to changing conditions without compromising integrity. Whether it's in medical devices or aerospace applications, the versatility of nitinol nickel titanium is reshaping our understanding of what materials can achieve.
As engineers increasingly embrace the capabilities of shape memory metals, we see a shift toward more efficient and effective solutions in design processes. The ability for these materials to return to predetermined shapes opens up new possibilities for creating compact devices that perform reliably under stress. This revolution is not merely theoretical; it's happening now, paving the way for advancements we once thought were science fiction.
Nitinol’s Impact on Future Technologies
The impact of nitinol on future technologies is profound and far-reaching. From enhancing medical procedures with minimally invasive tools to improving performance in aerospace missions, nitinol wire is at the forefront of innovation. Its unique properties make it ideal for applications that require both durability and adaptability—qualities that are increasingly sought after as technology evolves.
Emerging applications across industries promise even more groundbreaking uses for this remarkable shape memory alloy. As research delves deeper into its potential, we may find new ways to harness metal nitinol's capabilities in areas such as robotics or smart materials. The future is bright for these materials; their influence will undoubtedly extend beyond what we currently envision.
Why Shape Memory Alloys Matter
Shape memory alloys like nitinol matter because they offer solutions to some of today's most pressing engineering challenges. Their ability to change shape under different temperatures means they can perform tasks that would be impossible with conventional materials like steel wire alone. This adaptability makes them invaluable in sectors ranging from healthcare to aerospace engineering.
Moreover, the reliability and biocompatibility of nitinol alloys ensure their continued use in life-saving medical devices such as stents and heart valves—showing us just how critical these materials are in improving human health outcomes. As industries strive for lighter yet stronger components, metal nitinol stands out as a winner due to its corrosion resistance and weight reduction benefits over traditional options. In essence, understanding why shape memory alloys matter will be key as we navigate an increasingly complex technological landscape.

