Introduction

In the realm of modern engineering, the emergence of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators has revolutionized actuation systems across various industries. These innovative devices leverage the unique properties of shape memory alloys to deliver precise movements and responses, making them invaluable in applications ranging from robotics to aerospace. Understanding SMA actuators is crucial for engineers and designers aiming to harness their full potential in developing cutting-edge technologies.
Understanding SMA Actuators
Shape memory alloy actuators, often referred to as SMA wire actuators, are materials that can return to a predetermined shape when subjected to specific thermal conditions. This remarkable property allows them to convert thermal energy into mechanical work with impressive efficiency. By grasping how SMA actuators function, one can appreciate their versatility and effectiveness in creating dynamic systems that respond intelligently to environmental changes.
Importance of Design in Actuation
The design process for SMA actuators is not just a technical necessity; it’s an art form that determines how well these devices perform under varying conditions. Thoughtful design considerations can lead to significant enhancements in actuator efficiency, responsiveness, and durability. As engineers explore new possibilities within the realm of Shape Memory Alloy technology, they must prioritize innovative design strategies that maximize the capabilities of SMA wire actuators.
Role of Prototyping and Testing
Prototyping and testing are integral components in the development cycle of SMA actuators, allowing designers to refine their ideas before final production. Rapid prototyping techniques enable quick iterations that lead to optimized designs tailored for specific applications or challenges faced by engineers today. Rigorous testing ensures that these Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators meet reliability standards while functioning effectively even under extreme conditions.
What Are SMA Actuators?
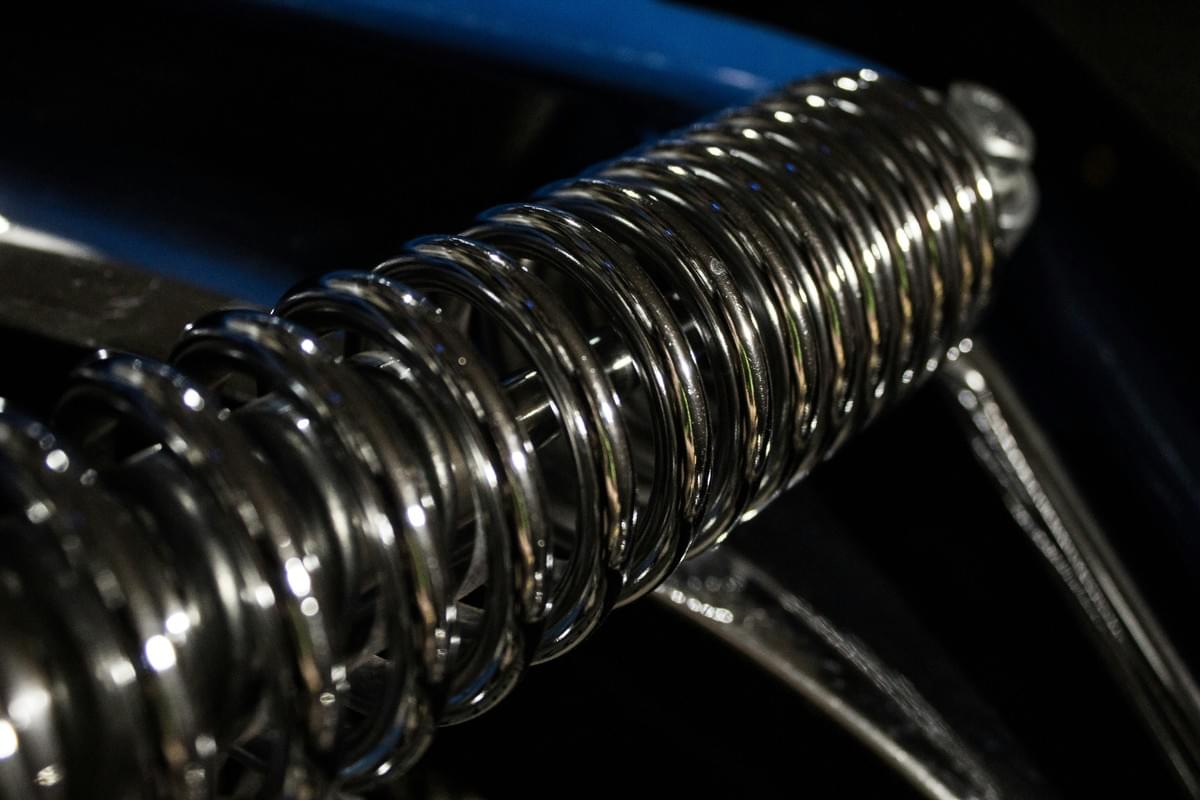

Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators are fascinating devices that leverage the unique properties of shape memory alloys to create motion in a controlled manner. These materials can remember a predetermined shape and return to it when subjected to specific stimuli, typically heat. This remarkable ability makes SMA actuators highly valuable in various applications, from robotics to medical devices.
Defining Shape Memory Alloys
Shape memory alloys are metallic materials that exhibit the remarkable ability to return to their original, pre-deformed shape when heated above a certain temperature. This phenomenon occurs due to a phase transformation within the alloy's crystalline structure, allowing it to switch between two distinct forms: martensite and austenite. The most common type of shape memory alloy used in SMA actuators is nickel-titanium (NiTi), renowned for its excellent performance characteristics and biocompatibility.
How SMA Wire Actuators Work
SMA wire actuators operate by utilizing the thermal expansion properties of shape memory alloys. When an electric current passes through the SMA wire, it heats up, causing the material to transition from its low-temperature martensitic state to its high-temperature austenitic state. This transformation produces significant contraction or expansion in the wire, enabling precise movement and actuation in various mechanisms.
Applications in Various Industries
The versatility of SMA actuators has led them into diverse industries where they perform critical functions. In robotics, these actuators provide lightweight solutions for movement without bulky motors or complex gears, enhancing efficiency and design flexibility. Similarly, in the medical field, SMA wire actuators are employed in minimally invasive surgical tools and stents that expand at body temperature—demonstrating their innovative potential across sectors.
The Design Process for SMA Actuators

Designing SMA actuators is a fascinating journey that blends engineering creativity with scientific principles. The unique properties of shape memory alloys (SMAs) offer a wealth of possibilities, but they also present specific challenges that must be addressed during the design process. By understanding key design considerations, embracing innovations in SMA technology, and collaborating with industry leaders like GEE SMA, engineers can create effective and efficient SMA wire actuators.
Key Design Considerations
When it comes to designing shape memory alloy actuators, several key considerations come into play. First and foremost is the selection of the appropriate type of shape memory alloy; different alloys have varying thermal properties and mechanical strengths that can significantly impact actuator performance. Additionally, factors such as actuator size, response time, and energy efficiency must be meticulously calculated to ensure optimal functionality in real-world applications.
Another crucial aspect is the thermal management of SMA wire actuators. Since these devices rely on temperature changes to activate their unique properties, effective heat dissipation and control mechanisms are essential for achieving precise actuation. Lastly, designers must consider integration with existing systems or products; ensuring compatibility can streamline development and enhance overall user experience.
Innovations in SMA Technology
The landscape of shape memory alloy technology is continually evolving, driven by innovative research and development efforts worldwide. Recent advancements have led to improved alloy compositions that enhance performance characteristics such as fatigue resistance and response times in SMA actuators. These innovations not only expand the operational capabilities of SMA wire actuators but also open doors for new applications across various industries.
Moreover, integrating smart materials with advanced control systems has created opportunities for more sophisticated actuation solutions. For instance, combining SMAs with sensors allows for real-time feedback during operation, leading to more accurate movement control. This synergy between innovation in materials science and cutting-edge electronics is revolutionizing how we think about actuation in modern machinery.
Collaborations with GEE SMA
Collaboration plays a pivotal role in advancing the design process for shape memory alloy actuators, particularly through partnerships with companies like GEE SMA. By leveraging their expertise in SMA technology and extensive industry knowledge, engineers can refine designs to meet specific application needs more effectively than ever before. Such collaborations often result in groundbreaking solutions that push the boundaries of what’s possible with SMA wire actuators.
GEE SMA's commitment to innovation means they are at the forefront of developing next-generation SMAs tailored for diverse applications—from robotics to aerospace engineering. Their collaborative approach fosters an environment where ideas flow freely between designers and researchers alike, leading to rapid prototyping cycles that bring concepts to life faster than traditional methods allow. This partnership model exemplifies how shared expertise can yield superior results while maximizing the potential of shape memory alloy technologies.
Prototyping SMA Actuators

Prototyping is a crucial step in the development of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators, as it allows engineers and designers to test ideas before full-scale production. The iterative nature of prototyping helps refine designs, ensuring that the final product meets performance standards and application needs. With advancements in technology, rapid prototyping techniques have become more accessible and efficient, paving the way for innovative SMA wire actuator designs.
Rapid Prototyping Techniques
Rapid prototyping techniques have revolutionized how SMA actuators are developed, enabling faster iterations and adjustments to design flaws. Techniques such as stereolithography (SLA) and selective laser sintering (SLS) allow for the quick creation of complex geometries that can closely mimic the final product's functionality. This speed not only reduces time-to-market but also enhances collaboration among teams working on Shape Memory Alloy projects by allowing immediate feedback on prototypes.
Moreover, these techniques facilitate testing various configurations of SMA wire actuators without committing to expensive production runs. By creating multiple prototypes quickly, engineers can experiment with different shapes, sizes, and material compositions to determine the most effective design for specific applications. Ultimately, rapid prototyping serves as a critical bridge between concept and reality in the world of SMA actuators.
Benefits of 3D Printing in SMA Development
3D printing has emerged as a game-changer in the development process of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators due to its versatility and efficiency. One significant advantage is its ability to produce intricate designs that traditional manufacturing methods may struggle with or find cost-prohibitive. This capability allows for innovative designs that capitalize on the unique properties of SMA materials while optimizing performance.
Another benefit is customization; 3D printing enables designers to create tailored solutions for specific applications without incurring substantial costs associated with tooling changes or mold creation. This flexibility is particularly beneficial when developing sma wire actuators for niche markets or specialized uses where standard solutions may fall short. Additionally, 3D printing supports rapid iteration cycles—designers can quickly modify their models based on testing feedback and reprint new prototypes within hours.
Lastly, using 3D printing significantly reduces material waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. This not only makes the process more environmentally friendly but also contributes to lower production costs over time—an essential factor when scaling up production runs for Shape Memory Alloy actuators aimed at mass markets.
Case Study: GEE SMA’s Prototyping Success
GEE SMA has set a benchmark in prototyping success by leveraging advanced techniques like rapid prototyping and 3D printing in their development processes for sma wire actuators. Their approach emphasizes collaboration between engineering teams during every stage—from conception through testing—to ensure that each prototype aligns with client specifications and industry standards effectively. One standout project involved designing an adaptive robotic arm utilizing Shape Memory Alloy technology; GEE's use of rapid iterations led to significant improvements in performance metrics after just a few rounds of refinement.
The company utilized both SLA and SLS technologies during this project, allowing them to create lightweight yet durable components that maximized efficiency while minimizing energy consumption—a critical requirement for many modern applications involving SMA actuators. The successful integration of these prototypes into real-world scenarios demonstrated not only GEE’s technical prowess but also showcased how innovative design could unlock new capabilities within existing frameworks.
In summary, GEE SMA's commitment to effective prototyping has solidified its reputation as an industry leader in developing cutting-edge Shape Memory Alloy solutions—proving that when it comes down to it, great ideas need great execution through thoughtful design processes and reliable testing methods.
Testing Solutions for SMA Actuators
Testing is a critical phase in the development of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators, ensuring that these innovative devices perform reliably under various conditions. Rigorous testing not only validates the design but also helps identify potential failure points, which is crucial for applications ranging from robotics to aerospace. Without thorough evaluation, the unique properties of SMA wire actuators may not translate into practical, real-world performance.
Importance of Rigorous Testing
Rigorous testing of SMA actuators is essential to guarantee their functionality and durability in demanding environments. The unique behavior of Shape Memory Alloys means that even minor design flaws can lead to significant performance issues when deployed in real-world applications. By implementing comprehensive testing protocols, developers ensure that SMA wire actuators operate efficiently and safely, meeting the high standards required across various industries.
Moreover, rigorous testing helps in fine-tuning the actuator's response to stimuli such as temperature changes or electrical inputs. This is particularly important since the effectiveness of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators hinges on their ability to return to a predetermined shape after deformation. Thus, consistent and thorough evaluations are paramount for achieving optimal performance and reliability.
Methods of Performance Evaluation
Evaluating the performance of SMA actuators involves several methods tailored to measure their specific characteristics effectively. One common approach includes thermal cycling tests, which assess how well an SMA wire actuator responds to repeated heating and cooling cycles—this simulates real operating conditions over time. Additionally, load tests are performed to determine how much force an actuator can exert while maintaining its shape memory capabilities.
Another effective method is fatigue testing, which evaluates how many cycles an actuator can endure before failure occurs; this is critical for applications where longevity is paramount. By combining these techniques with advanced data acquisition systems, engineers can gather valuable insights into how Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators behave under stress and strain. Ultimately, these performance evaluations inform design improvements and enhance overall product reliability.
Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Conditions
Ensuring reliability in extreme conditions poses a significant challenge for developers working with SMA actuators; however, it’s crucial for many applications like aerospace and medical devices where failure could have catastrophic consequences. To address this challenge, extensive environmental testing simulates extreme temperatures or humidity levels that an actuator might encounter during its lifecycle. This helps validate that the SMA wire actuator maintains its shape memory properties even when faced with adverse conditions.
Moreover, integrating redundancy into designs can further enhance reliability by providing backup systems should one component fail during operation—this strategy is often employed in critical applications like robotics or automotive systems where safety cannot be compromised. Additionally, ongoing monitoring technologies can provide real-time feedback on an actuator's health status throughout its operational life cycle.
In conclusion, rigorous testing solutions play a vital role in ensuring that Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuators meet industry demands for reliability and performance under varying conditions—making them indispensable components across numerous fields.
Future Trends in SMA Technology
The future of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) technology is brimming with potential. As industries continue to explore the capabilities of SMA actuators, we are witnessing a surge in innovative applications and markets that leverage their unique properties. From robotics to aerospace, the versatility of SMA wire actuators is paving the way for groundbreaking advancements.
Emerging Applications and Markets
SMA actuators are making waves across various sectors, particularly in robotics and medical devices. For instance, in soft robotics, these shape memory alloys enable robots to mimic natural movements, enhancing their functionality and adaptability. Additionally, SMA technology is gaining traction in the automotive industry for applications like adaptive seating and active suspension systems, offering improved comfort and performance.
Moreover, the medical field is embracing SMA wire actuators for minimally invasive surgical tools that can change shape or stiffness on demand. This adaptability not only enhances precision but also minimizes patient recovery time. As new markets emerge, we can expect more inventive uses for Shape Memory Alloy technology that will redefine standards across industries.
Advancements in Shape Memory Alloys
Recent advancements in materials science are pushing the boundaries of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) capabilities further than ever before. Researchers are developing new alloy compositions that enhance thermal response times while improving fatigue resistance—key factors for ensuring longevity and reliability in SMA wire actuators. These innovations promise to make SMAs even more efficient, allowing them to perform complex tasks with greater ease.
Additionally, smart materials integrating sensors with SMA technology are on the rise; this combination allows real-time monitoring and feedback during operation. Such integration can lead to self-adjusting systems that optimize performance based on environmental conditions or operational demands. The continuous evolution of these materials signifies a promising horizon for SMA actuators as they become integral components of advanced technological solutions.
GEE SMA’s Role in Shaping the Future
GEE SMA is at the forefront of these exciting developments within the world of shape memory alloys. By investing heavily in research and development, GEE has positioned itself as a leader not only in manufacturing high-quality SMA actuators but also in pioneering innovative applications tailored to market needs. Their commitment to collaboration with industry partners ensures that they remain aligned with emerging trends while pushing boundaries further.
Furthermore, GEE's focus on sustainability reflects a growing trend towards eco-friendly technologies within manufacturing processes involving SMAs. By optimizing production methods and sourcing raw materials responsibly, GEE aims to set an example within the industry while contributing positively to global sustainability goals. As a trailblazer in this space, GEE SMA is undoubtedly shaping a future where shape memory alloy applications will revolutionize how we think about actuation technologies.
Conclusion

As we wrap up our exploration of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) Actuators, it’s clear that these remarkable devices hold enormous potential across various industries. With their unique properties and versatile applications, SMA actuators can revolutionize how we approach actuation in robotics, aerospace, and biomedical fields. By maximizing the potential of SMA wire actuators, we can create more efficient systems that enhance performance and reliability.
Maximizing the Potential of SMA Actuators
To truly harness the capabilities of SMA actuators, ongoing research and development are crucial. Engineers and designers must collaborate to refine existing technologies while exploring innovative applications for Shape Memory Alloys. By pushing the boundaries of what SMA wire actuators can do, we pave the way for groundbreaking advancements that could redefine entire industries.
Enhancing Design for Optimal Performance
Design plays a pivotal role in ensuring that SMA actuators perform at their best. Factors such as material selection, geometry optimization, and thermal management are vital to achieving optimal functionality from Shape Memory Alloy devices. By focusing on these design considerations, engineers can develop more efficient SMA wire actuators that not only meet but exceed performance expectations.
The Future of Shape Memory Alloy Applications
Looking ahead, the future of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) Actuators is filled with exciting possibilities. Emerging markets such as soft robotics and wearable technology are ripe for innovation with these smart materials at their core. As companies like GEE SMA continue to lead in this field, we can expect to see an expansion in applications that leverage the unique properties of SMA wire actuators to solve complex challenges.

