Introduction

Welcome to the fascinating world of shape memory actuators, where materials possess the extraordinary ability to remember their original shapes. These remarkable devices, primarily made from shape memory alloys (SMAs), are revolutionizing various industries with their unique properties and functionalities. As we delve deeper into the realm of memory materials, we'll uncover how these innovations are not just theoretical concepts but practical solutions that enhance our everyday lives.
The Magic of Shape Memory Actuators
The allure of shape memory actuators lies in their ability to transform mechanical energy into motion through changes in temperature. When exposed to specific thermal conditions, a shape memory alloy actuator can revert to its pre-defined shape, enabling precise movements and applications in various fields. This magical transformation is what makes SMA actuators indispensable for engineers and designers looking for innovative solutions.
Unpacking Shape Memory Alloys
Shape memory alloys are a class of metallic materials that exhibit a unique phase transformation behavior, allowing them to return to a predetermined shape when heated above a certain temperature. Commonly used SMAs include Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium known for its exceptional properties such as high strength and corrosion resistance. Understanding the science behind these memory materials is crucial for appreciating their role in modern technology.
Real-World Applications of Memory Materials
The versatility of shape memory materials has led to their adoption across numerous sectors including aerospace, medical devices, and robotics. In aerospace applications, SMA actuators help control wing flaps and other components with precision while minimizing weight—a critical factor in flight efficiency. Similarly, in the medical field, these innovative materials enable minimally invasive procedures through devices that can change shape within the human body, showcasing just how impactful shape memory actuators can be on our lives.
What Are Shape Memory Actuators?
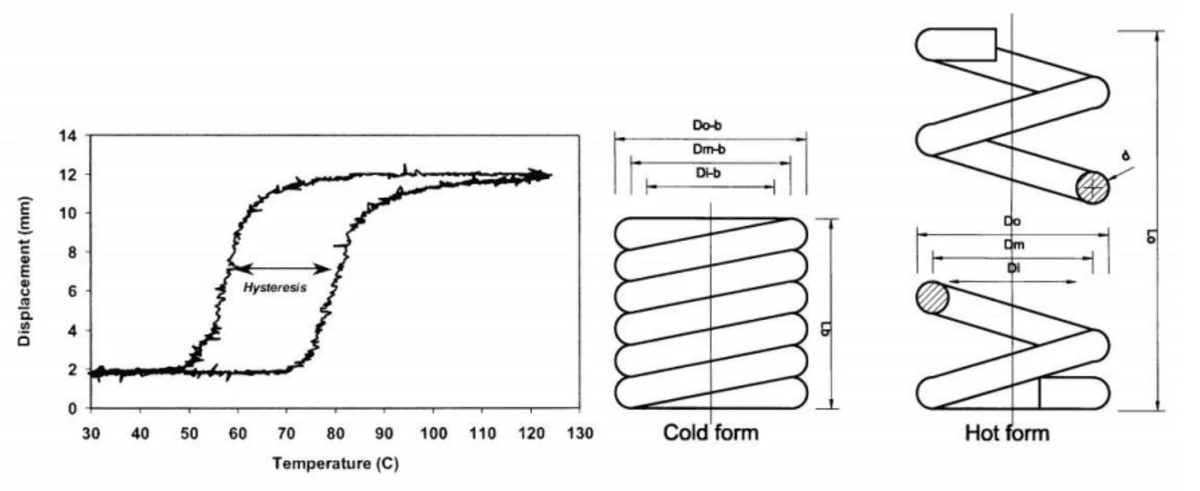
Shape memory actuators are fascinating devices that leverage the unique properties of shape memory alloys (SMAs) to create movement and force in a controlled manner. These materials have the remarkable ability to return to a predetermined shape when subjected to specific stimuli, such as changes in temperature. This characteristic makes shape memory actuators an exciting area of research and application across various industries.
Defining Shape Memory Alloys
Shape memory alloys are special metallic materials that possess the ability to remember their original shapes after being deformed. When cooled or heated beyond certain temperatures, these alloys can undergo phase transformations, allowing them to revert back to their pre-deformed state. The most commonly used shape memory alloy is Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium known for its impressive mechanical properties and biocompatibility.
How SMA Actuators Work
SMA actuators operate on the principle of thermal activation, where changes in temperature trigger the transformation between different phases of the material. When heat is applied, the SMA transitions from a martensitic (deformed) phase to an austenitic (original) phase, resulting in movement or force generation. This process can be finely controlled by adjusting the temperature and can produce significant mechanical work from a relatively small actuator size.
Advantages of Using Memory Materials
The advantages of using shape memory materials like SMAs are numerous and compelling for engineers and designers alike. First, their compact size allows for innovative designs that save space without sacrificing performance; this is particularly beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as aerospace engineering. Additionally, SMA actuators offer high energy density and reliability, making them ideal for long-term applications where maintenance may be challenging.
GEE SMA: The Leader in Shape Memory Technology

In the world of shape memory technology, GEE SMA stands out as a pioneer, driving innovations that enhance the capabilities and applications of shape memory actuators. This company has made significant strides in developing advanced shape memory alloys (SMAs) that are not only efficient but also versatile across various industries. With a commitment to research and development, GEE SMA is setting new standards for what memory materials can achieve.
Overview of GEE SMA
GEE SMA specializes in the production and application of high-performance shape memory alloys, particularly Nitinol, which is renowned for its exceptional properties. Founded by a team of engineers and researchers passionate about material science, GEE SMA quickly gained recognition for its innovative approaches to creating reliable and effective shape memory actuators. Their products are designed to meet rigorous industry standards while providing solutions that enhance performance and efficiency in real-world applications.
Innovations in Nitinol Production
One of the hallmarks of GEE SMA's success is its focus on pioneering advancements in Nitinol production techniques. By refining manufacturing processes, they have improved the quality and consistency of their shape memory alloy products, resulting in superior performance characteristics for their SMAs. These innovations not only boost the effectiveness of their shape memory actuators but also allow for more complex designs that can adapt to diverse operational environments.
Contribution to Space Missions
GEE SMA's influence extends beyond terrestrial applications; their shape memory materials play a vital role in space missions as well. The unique properties of Nitinol make it an ideal choice for aerospace components that require reliability under extreme conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and vacuum environments. By integrating advanced shape memory actuators into spacecraft systems, GEE SMA contributes significantly to mission success and safety, showcasing how these innovative materials can push the boundaries of exploration.
Industries Harnessing Shape Memory Alloys

Shape memory alloys (SMAs) are revolutionizing various industries, offering innovative solutions that were previously unimaginable. Their unique properties make them ideal for applications ranging from aerospace to medical devices and robotics. Let’s dive deeper into how shape memory actuators are making waves in these sectors.
Aerospace Applications
In the aerospace industry, shape memory actuators play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and performance. These memory materials can adapt to changing conditions, allowing for dynamic adjustments in aircraft components such as wing flaps and landing gear systems. The ability of shape memory alloy actuators to return to their original shape after deformation means lighter designs that can withstand extreme conditions without compromising safety.
Moreover, the use of SMA actuators can lead to significant weight reductions in aircraft structures, which is essential for fuel efficiency. By incorporating these advanced materials, aerospace engineers are paving the way for more sustainable flight solutions. As the industry pushes towards greener alternatives, the adaptability of shape memory alloys positions them as key players in future aviation innovations.
Medical Device Innovations
The medical field has embraced shape memory alloys with open arms, thanks to their remarkable versatility and reliability. Shape memory alloy actuators are commonly found in devices such as stents and surgical tools, where precise movement is vital for patient safety and treatment efficacy. The unique properties of SMAs allow them to be minimally invasive while still providing maximum functionality—an essential trait in modern medicine.
Additionally, advancements in SMA technology have led to breakthroughs in prosthetics and orthopedic devices that mimic natural movement more closely than ever before. This not only improves patient comfort but also enhances overall outcomes during rehabilitation processes. As researchers continue exploring new applications for these innovative materials, we can expect even more transformative changes in healthcare delivery.
Robotics and Automation
In the realm of robotics and automation, shape memory alloys are redefining what machines can do with their incredible responsiveness and adaptability. SMA actuators enable robots to perform complex tasks with precision by mimicking human-like movements while remaining lightweight and efficient. This capability is particularly advantageous in environments where traditional motors may struggle due to size or weight constraints.
Furthermore, the integration of shape memory materials into robotic systems allows for greater flexibility when it comes to design choices—think soft robotics that can safely interact with humans or delicate objects without causing damage! As industries increasingly adopt automation technologies, the potential applications for SMAs seem almost limitless—from manufacturing lines to autonomous vehicles navigating unpredictable terrains.
The Mechanics Behind Memory Alloys
The fascinating world of shape memory alloys (SMAs) is grounded in the intricate mechanics that govern their unique behaviors. At the heart of these materials lies a remarkable phase transformation process, particularly evident in Nitinol, a popular type of shape memory alloy. Understanding this transformation is crucial for harnessing the full potential of shape memory actuators across various applications.
Phase Transformation in Nitinol
Nitinol exhibits two primary phases: the austenite phase and the martensite phase, each with distinct properties. When a shape memory alloy actuator is cooled below its transformation temperature, it adopts a more malleable martensitic structure, allowing for easy deformation. Upon heating above this threshold, Nitinol reverts to its original austenitic form, effectively remembering its predetermined shape and enabling powerful movement—a feature that makes SMA actuators incredibly versatile.
This phase transformation not only allows for significant mechanical work but also enables precise control over motion and force generation in various applications. The ability to switch between these two phases is what underpins the functionality of many devices relying on shape memory materials. This dynamic capability has led to innovative designs in robotics, medical devices, and aerospace technologies.
Unique Properties of Shape Memory Materials
Shape memory materials are celebrated for their unique properties that distinguish them from conventional materials. Among these characteristics are high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent fatigue resistance—qualities that make them ideal candidates for use in demanding environments like aerospace and medical fields. Additionally, their ability to undergo large deformations while maintaining structural integrity showcases their exceptional resilience.
Another noteworthy property is superelasticity; when subjected to stress above a certain threshold at elevated temperatures, SMAs can undergo significant strain without permanent deformation. This means that once the load is removed, they return to their original shape effortlessly—an invaluable trait for applications requiring reliable performance under varying conditions. These unique features position shape memory alloys as transformative solutions across multiple industries.
Engineering Challenges and Solutions
While the advantages of using shape memory alloys are compelling, engineering challenges persist in optimizing their performance within practical applications. One significant hurdle involves controlling the temperature range at which phase transformations occur; variations can lead to unpredictable behavior in SMA actuators if not properly managed. Engineers must carefully calibrate these parameters to ensure reliability and functionality across different environments.
Another challenge lies in manufacturing consistent quality within SMA components; defects or inconsistencies can severely impact performance outcomes and longevity of products utilizing these materials. Advanced processing techniques such as heat treatment or specialized alloy compositions have been developed as solutions to enhance material uniformity and durability over time. By addressing these engineering challenges head-on, researchers continue pushing boundaries on what’s possible with shape memory materials.
Future Trends in SMA Actuators

As we look to the future, the landscape of shape memory actuators is poised for remarkable transformation. Advancements in material science promise to enhance the capabilities of shape memory alloys, making them even more versatile and efficient. With ongoing research and innovation, these memory materials will likely revolutionize industries beyond our current imagination.
Advancements in Material Science
Material science is at the forefront of enhancing shape memory alloys, particularly Nitinol, which has gained popularity due to its unique properties. Researchers are exploring new compositions and treatments that could improve the performance of SMA actuators under various conditions. This includes increasing their fatigue resistance and expanding their operational temperature range, which would significantly broaden their application potential across different sectors.
In addition to improving existing materials, scientists are also investigating entirely new classes of shape memory materials that could outperform traditional SMAs in specific applications. These advancements may lead to lighter weight options or even more responsive actuators that can adapt dynamically to environmental changes. As these innovations unfold, we can expect a surge in demand for advanced shape memory alloy actuators that meet increasingly complex engineering challenges.
Expanding Applications Across Industries
The versatility of shape memory alloys means they are finding applications in an ever-growing array of industries beyond aerospace and medical devices. For instance, automotive manufacturers are beginning to incorporate SMA actuators into their designs for adaptive components that enhance vehicle performance and safety features. Similarly, consumer electronics are leveraging these innovative materials for everything from self-adjusting mechanisms in smartphones to smart home devices.
Moreover, the robotics sector stands to benefit immensely from the flexibility offered by SMA actuators; they can enable robots to perform intricate movements with precision while reducing overall system weight. As industries continue exploring how best to integrate these remarkable memory materials into their products, we will likely see a proliferation of novel applications that enhance functionality and user experience across various domains.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Developments
As global awareness about sustainability grows, so does interest in eco-friendly developments within the realm of shape memory alloys. Researchers are focusing on creating more sustainable production methods for SMAs while ensuring that these processes minimize waste and energy consumption. By harnessing renewable resources or recycling existing materials into new shapes or forms, manufacturers can reduce their environmental footprint while still delivering high-performance shape memory actuators.
Furthermore, as consumers increasingly demand environmentally responsible products, companies incorporating sustainable practices into their design processes will gain a competitive edge in the market. The ability to produce efficient SMA actuators with reduced environmental impact aligns perfectly with contemporary trends toward green technology solutions across all sectors—from manufacturing to consumer goods—ensuring a brighter future for both businesses and our planet.
Conclusion
Shape memory actuators are revolutionizing the way we think about movement and functionality in various applications. With their unique ability to return to a predetermined shape when exposed to specific stimuli, these remarkable devices have proven invaluable across multiple industries. The versatility and efficiency of shape memory alloys (SMAs) make them a go-to choice for engineers and innovators alike.
Key Benefits of Shape Memory Actuators
The key benefits of shape memory actuators lie in their unparalleled adaptability and reliability. These memory materials can undergo significant deformation yet revert to their original form with precision, making them ideal for applications requiring exact movements. Additionally, SMA actuators often consume less energy compared to traditional systems, enhancing overall efficiency and sustainability.
GEE SMA's Impact on Innovation
GEE SMA stands at the forefront of innovation in the realm of shape memory technology, setting benchmarks that others aspire to reach. Their advancements in nitinol production have not only improved the performance of shape memory alloys but also expanded their potential applications in fields like aerospace and medical devices. By continually pushing the envelope, GEE SMA is ensuring that shape memory actuators remain at the cutting edge of technology.
The Future of Shape Memory Materials
The future of shape memory materials looks incredibly promising as research continues to unlock new possibilities for SMAs across diverse sectors. Innovations in material science are paving the way for even more efficient and versatile shape memory alloy actuators that could transform industries from robotics to healthcare. As sustainability becomes a priority, eco-friendly developments in these materials will further enhance their appeal and application potential.

