Introduction
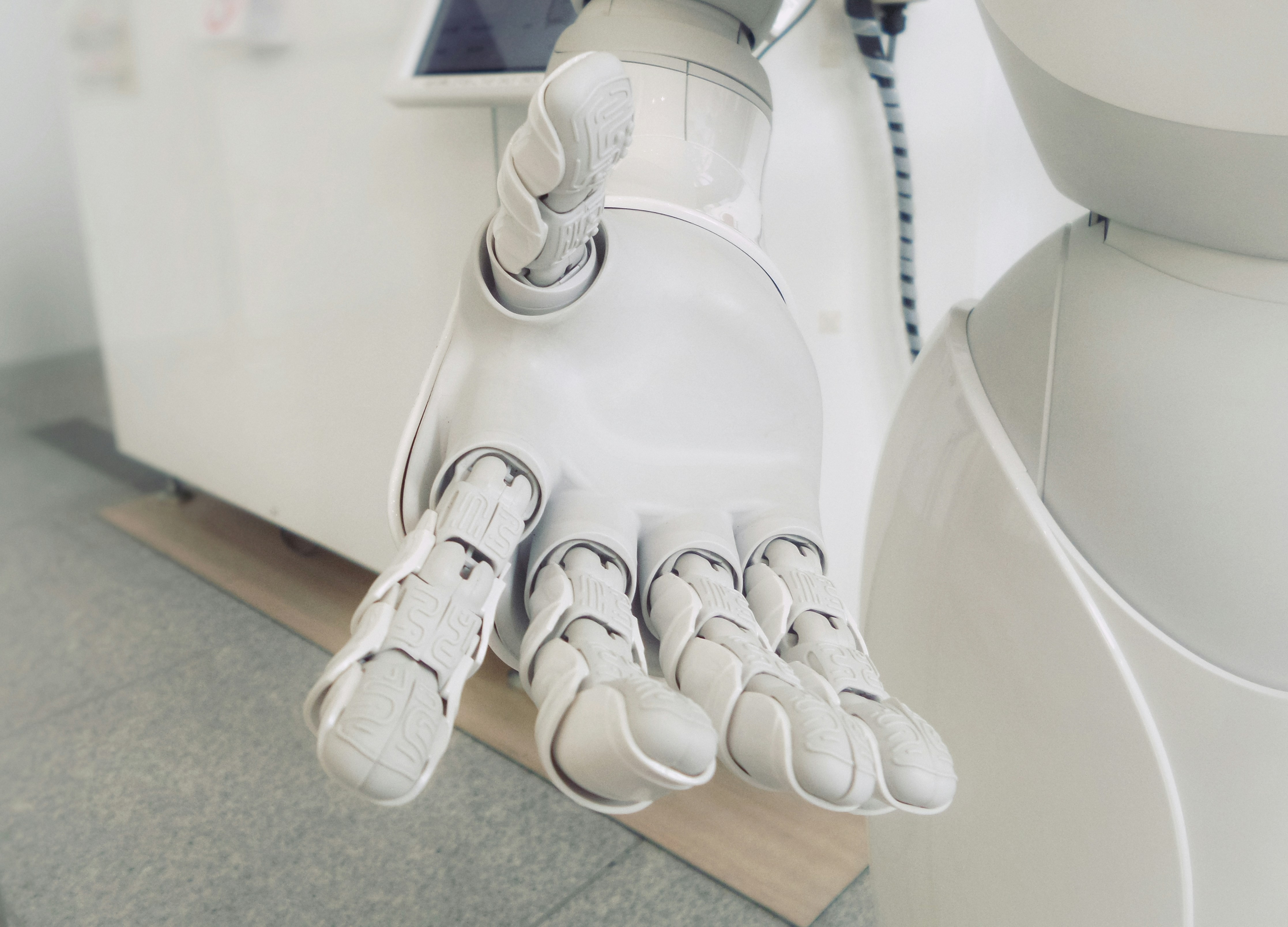

In the realm of robotics, the magic behind shape memory actuators is nothing short of revolutionary. These remarkable devices, particularly SMA wire actuators and SMA motors, offer unique capabilities that transform how robots interact with their environment. By harnessing the extraordinary properties of shape memory alloys, engineers are crafting solutions that were once limited to science fiction.
The Magic Behind Shape Memory Actuators
Shape memory actuators possess a fascinating ability: they can return to a predetermined shape when heated or cooled. This characteristic allows for compact designs and lightweight components, making them ideal for applications where space and weight are critical factors. From robotic limbs to precision tools, SMA actuators enable innovative movements that enhance functionality in ways traditional systems cannot match.
Why Robotics Needs SMA Technology
As robotics continues to evolve, the demand for more efficient and adaptable technologies grows stronger. SMA technology fills this gap by providing actuators that can mimic natural movements with precision and speed while consuming less power than conventional motors. The integration of shape memory actuators into robotic systems not only improves performance but also opens up new possibilities for automation across various industries.
The Science of Shape Memory Alloys
At the heart of these advanced devices lies the science of shape memory alloys (SMAs), particularly nitinol—a nickel-titanium alloy known for its exceptional flexibility and strength. When subjected to different temperatures, nitinol undergoes phase transformations that allow it to remember its original form after deformation. This unique property makes nitinol linear actuators ideal candidates for applications ranging from medical devices to aerospace engineering.
Understanding Shape Memory Alloys

Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) are a fascinating class of materials that can remember their original shape when subjected to changes in temperature. These materials undergo a unique phase transformation, transitioning between two distinct crystalline structures: the austenite phase at high temperatures and the martensite phase at lower temperatures. This ability to revert to a predetermined shape makes SMAs particularly valuable in various applications, especially in robotics where precision and adaptability are crucial.
What Are Shape Memory Alloys
At their core, shape memory alloys are metallic compounds that exhibit the remarkable property of returning to their original configuration after deformation when heated above a certain temperature threshold. This transformation is not just limited to metals; it has been harnessed in various forms, including SMA wire actuators and SMA motors. The most commonly used SMA is Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium, which has gained fame for its effectiveness in creating reliable shape memory actuators.
The magic behind these alloys lies in their microstructure and phase changes. When an SMA wire actuator is deformed while in its martensitic state, it can be straightened or bent into different shapes; however, upon heating it back up, the material returns to its initial form with impressive force. This property opens up new avenues for innovation across multiple industries.
Unique Properties of Nitinol
Nitinol stands out among other SMAs due to its exceptional characteristics such as superelasticity and biocompatibility. Superelasticity allows Nitinol to undergo significant strain without permanent deformation when subjected to stress at temperatures above its transformation point, making it highly versatile for applications requiring flexibility and resilience—ideal traits for an SMA motor or actuator in robotics!
Moreover, Nitinol's biocompatibility makes it suitable for medical applications as well as robotic technologies where interaction with humans or delicate environments is essential. This unique combination of properties enables nitinol linear actuators to be integrated seamlessly into robotic systems that require both strength and sensitivity.
The ability of Nitinol to operate effectively under varying conditions further solidifies its role as a backbone material for innovative robotic solutions ranging from prosthetics to automated systems.
Applications in Robotics
Shape memory actuators have found numerous applications within the realm of robotics thanks to their lightweight nature and high power-to-weight ratio compared with traditional motors. One prominent application includes soft robotics where flexibility is paramount; here, SMA wire actuators are utilized for creating adaptive grippers that can manipulate objects delicately without causing damage.
Furthermore, nitinol linear actuators have been employed in robotic arms designed for intricate tasks such as surgery or assembly lines where precision movement is critical. These actuators allow robots not only to perform tasks more efficiently but also adaptively respond to changing environments by adjusting their shapes on-the-fly based on real-time data inputs.
In addition to these applications, advancements continue as researchers explore new ways to integrate shape memory technology into various robotic functions—paving the way for smarter machines capable of mimicking human-like movements with unprecedented accuracy.
The Versatility of SMA Wire Actuators

Shape memory actuators have carved a niche in the world of robotics, showcasing remarkable versatility through SMA wire actuators. These unique devices leverage the properties of shape memory alloys, particularly Nitinol, to convert thermal energy into mechanical motion. This transformation allows for precise movement and control in applications ranging from medical devices to aerospace technology.
How SMA Wire Actuators Work
At the heart of every SMA wire actuator lies the fascinating behavior of shape memory alloys, specifically Nitinol. When heated above a certain temperature, these materials undergo a phase transformation that allows them to return to their original shape after being deformed. This simple yet effective mechanism enables SMA motors to generate significant force while maintaining lightweight and compact designs, making them ideal for various robotic applications.
The operation of an SMA actuator is straightforward: as electrical current passes through the wire, it heats up and contracts, performing work against a load or moving components within a robotic system. Upon cooling down, the wire returns to its elongated state, ready for another cycle. This on-demand actuation not only enhances energy efficiency but also reduces wear and tear compared to traditional motors.
Industries Utilizing SMA Wire Actuators
SMA wire actuators are making waves across multiple industries due to their unique advantages over conventional actuation methods. In healthcare, these shape memory actuators are employed in minimally invasive surgical tools that require delicate movements while being compact enough for use in tight spaces. The aerospace industry also benefits from SMA technology by utilizing Nitinol linear actuators for applications like adaptive wing structures that enhance aircraft performance.
Robotics is another field where SMA motors shine brightly; they enable agile locomotion in soft robots and provide precise control in robotic arms used for assembly tasks. Automotive manufacturers have also started integrating SMA actuators into systems like active suspension controls and smart seat adjustments, leading to improved passenger comfort and safety features. As industries continue discovering new applications for these innovative devices, the future looks bright for shape memory technology.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Several successful implementations showcase how versatile SMA wire actuators can be across different sectors. For instance, researchers at MIT developed a soft robotic gripper powered by an SMA actuator that can gently pick up fragile objects without causing damage—a game-changer in logistics and handling sensitive materials. Another notable example comes from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), where Nitinol linear actuators were integrated into deployable structures on spacecraft such as Mars rovers.
In medical technology, companies like Medtronic have utilized shape memory actuators in stents that expand upon reaching body temperature—providing life-saving interventions with minimal invasiveness. These case studies highlight not only the adaptability of SMA motors but also their potential impact on improving efficiency and functionality across various applications within robotics and beyond.
Innovations in SMA Motors
The world of robotics is witnessing a remarkable transformation thanks to innovations in shape memory actuators (SMAs). These advancements are largely driven by the design and functionality of SMA motors, which harness the unique properties of shape memory alloys like Nitinol. With their ability to convert thermal energy into mechanical motion, SMA motors are proving to be game-changers across various applications.
Breakthroughs in SMA Motor Design
Recent breakthroughs in SMA motor design have led to enhanced performance and efficiency, making them more viable for diverse robotic applications. Engineers have been experimenting with different configurations of SMA wire actuators, optimizing their geometry and material composition to achieve higher output forces while minimizing energy consumption. These advancements not only improve the lifespan of shape memory actuators but also expand their usability beyond traditional limits.
Moreover, innovative control systems are being developed alongside these new designs, enabling precise manipulation of the SMA actuator's movements. This synergy between design and control technology allows for smoother operation and better integration into complex robotic systems. As a result, we are seeing an increase in the adoption of nitinol linear actuators that can perform intricate tasks previously thought impossible for conventional motors.
Performance Comparisons with Traditional Actuators
When comparing shape memory actuators with traditional electric or pneumatic actuators, it's clear that SMAs offer unique advantages that can’t be overlooked. For instance, while traditional actuators may require bulky components and extensive maintenance, SMA motors provide a compact solution with fewer moving parts. This simplicity translates to lighter robotic designs that enhance overall mobility without sacrificing performance.
Additionally, performance metrics such as response time and energy efficiency favor SMA technology significantly; they can operate on minimal power while delivering impressive force outputs. In many cases, this leads to longer operational times for robots powered by SMA wire actuators compared to those reliant on conventional systems. The ability of shape memory actuators to return to their original form after deformation also means less wear over time—another win for durability.
Real-World Applications in Robotics
The real-world applications of innovations in SMA motors are vast and varied; from medical devices to aerospace technology, these versatile components are making waves across industries. In robotics specifically, we see them employed in soft robotics where flexibility is paramount—think grippers that adapt seamlessly around objects or surgical tools that navigate delicate tissues precisely due to the responsive nature of nitinol linear actuators.
Moreover, industries such as automotive manufacturing leverage shape memory actuators for automated processes requiring swift adjustments under varying conditions—think adjustable seats or mirrors responding intuitively based on user preferences or environmental factors! As research continues into optimizing these remarkable devices further, it’s evident that the future holds even more exciting possibilities for integrating SMAs into advanced robotic solutions.
Nitinol Linear Actuators: The Future of Motion

Nitinol linear actuators are revolutionizing the field of motion control in robotics, thanks to their unique properties and advantages. These shape memory actuators utilize the remarkable characteristics of Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy that can remember its original shape after deformation. With their ability to convert thermal energy into mechanical work, nitinol linear actuators are paving the way for more efficient and compact robotic systems.
Advantages of Nitinol Linear Actuators
One of the standout advantages of nitinol linear actuators is their lightweight design, which makes them ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor. Unlike traditional actuators, these SMA wire actuators can achieve significant motion with minimal mass, enabling robots to be more agile and energy-efficient. Additionally, the inherent flexibility and durability of Nitinol mean that these SMA motors can withstand a range of environmental conditions without compromising performance.
Another key benefit lies in their low power consumption compared to conventional motors. This efficiency not only prolongs battery life in mobile robots but also reduces heat generation during operation—an important consideration for sensitive applications. Furthermore, nitinol linear actuators boast quieter operation than many traditional alternatives, making them suitable for use in environments where noise reduction is essential.
Integration with Modern Robotics
The integration of nitinol linear actuators into modern robotics has been nothing short of transformative. As engineers seek to create more compact and efficient designs, these shape memory actuators provide a solution that allows for innovative configurations previously thought impossible. By incorporating SMA technology into robotic systems, designers can achieve greater precision and responsiveness while minimizing overall system complexity.
Moreover, the adaptability of nitinol linear actuators enables seamless integration with existing robotic frameworks. Whether it's enhancing dexterity in robotic arms or providing actuation in soft robotics applications, these SMA actuators offer versatility that traditional motors struggle to match. This compatibility extends across various platforms—from industrial robots to consumer electronics—paving the way for widespread adoption and innovation.
Examples from the Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry has been quick to embrace nitinol linear actuators due to their performance advantages in demanding environments. For instance, NASA has explored using shape memory actuators in spacecraft systems where reliability and weight savings are paramount factors. In one notable project involving satellite deployment mechanisms, SMA wire actuators demonstrated exceptional precision while significantly reducing overall system weight compared to traditional actuation methods.
Additionally, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have also benefited from integrating SMA technology into their design processes. The ability to create lightweight control surfaces using nitinol linear actuators allows UAVs to achieve superior maneuverability without sacrificing structural integrity or payload capacity. These advancements highlight how shape memory actuator technology is shaping the future of aerospace engineering by enabling new capabilities that were once merely theoretical.
GEE SMA: Powering Robotic Advances

In the ever-evolving world of robotics, GEE SMA has emerged as a key player in advancing technologies that utilize shape memory actuators. These innovative devices leverage the unique properties of shape memory alloys (SMAs) to create dynamic movements and responses in robotic systems. As we delve into GEE SMA's impact, it becomes clear that their contributions are not just incremental but transformative for the field.
Overview of GEE SMA's Impact
GEE SMA has pioneered advancements in the development of shape memory actuators, particularly with their focus on nitinol linear actuators and sma wire actuators. Their commitment to research and innovation has led to breakthroughs that enhance performance and reliability in various applications, from industrial automation to medical devices. By integrating cutting-edge technology with traditional actuator designs, GEE SMA is reshaping how we think about motion and control in robotics.
The versatility of the sma motor design has allowed for a wide range of applications across multiple industries. Whether it's creating more efficient robotic limbs or developing compact actuation systems for drones, GEE SMA's influence is evident everywhere you look. Their work doesn't just improve existing technologies; it opens doors to new possibilities that were once thought impossible.
Role in Significant Space Missions
One of the most exciting aspects of GEE SMA's work is its application in significant space missions where reliability and precision are paramount. Shape memory actuators have been instrumental in controlling mechanisms on spacecraft, such as deploying solar panels or adjusting antennas with unparalleled accuracy. The lightweight nature of nitinol linear actuators makes them ideal for aerospace applications where every gram counts.
For instance, during recent Mars exploration missions, sma wire actuators were utilized to operate scientific instruments remotely while ensuring minimal energy consumption—a critical factor when dealing with limited power sources in space travel. The ability of these shape memory actuators to operate effectively under extreme conditions showcases their robustness and adaptability, making them invaluable assets for future explorations beyond our planet.
GEE SMA’s contributions don’t stop at current missions; they are also laying the groundwork for future endeavors aimed at deeper space exploration. With ongoing advancements and refinements, we can expect even more sophisticated uses of SMAs that will push the boundaries of what is achievable in space technology.
Future Prospects for GEE SMA in Robotics
Looking ahead, the future prospects for GEE SMA within robotics appear incredibly promising as they continue to innovate within this niche market by refining their existing products like sma motors and exploring new avenues such as soft robotics applications powered by shape memory actuators. The potential integration of these advanced technologies into everyday robotic systems could revolutionize industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare.
Moreover, ongoing research into enhanced materials and designs will likely lead to even more efficient nitinol linear actuators capable of achieving complex motions with greater precision than ever before. As robots become increasingly integrated into our daily lives—whether through automation or assistance—GEE SMA stands poised at the forefront, ready to meet evolving demands with their state-of-the-art solutions.
In conclusion, as we envision a future filled with intelligent machines capable of performing intricate tasks seamlessly alongside humans, it’s clear that companies like GEE SMA will play an integral role through their innovations centered around shape memory technology—ensuring that robotics continues its journey towards unprecedented capabilities.
Conclusion

As we draw the curtain on our exploration of shape memory actuators, it’s clear that these remarkable devices are poised for a bright future. The evolution of SMA technology heralds a new era in robotics, where efficiency and adaptability are paramount. With ongoing research and development, we can expect even more innovative applications that harness the unique properties of shape memory alloys.
The Future of Shape Memory Actuators
The future of shape memory actuators looks promising, with advancements in materials and design paving the way for broader applications. SMA wire actuators are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing for greater precision and control in robotic systems. As industries continue to embrace automation, the demand for reliable SMA motors will undoubtedly rise, driving further innovation in this exciting field.
How SMA Technology Enhances Robotics
SMA technology enhances robotics by providing lightweight solutions that can perform complex tasks with minimal energy consumption. The ability of a shape memory actuator to return to its original shape when heated allows for compact designs that can fit into tight spaces without sacrificing functionality. This versatility not only improves robot performance but also opens doors to new possibilities in fields such as medical robotics and aerospace.
GEE SMA's Role in Innovation
GEE SMA has emerged as a key player in advancing the capabilities of shape memory actuators within various sectors. Their contributions have been instrumental in significant space missions, demonstrating how nitinol linear actuators can withstand extreme conditions while delivering exceptional performance. As GEE SMA continues to innovate, we can anticipate groundbreaking developments that will further integrate SMA technology into the future landscape of robotics.

