Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of engineering and technology, Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) have emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing how we approach design and functionality. These remarkable materials can return to a predefined shape when heated, making them the backbone of innovative solutions across various industries. The rise of SMA technology is not just a trend; it’s a testament to human ingenuity in creating smarter, more efficient systems.
The Rise of Shape Memory Alloys
The journey of shape memory alloys began in the 1960s with the discovery of Nitinol, an alloy composed primarily of nickel and titanium. This unique material exhibits an incredible ability to remember its original form after deformation, leading to groundbreaking applications in fields such as robotics, aerospace, and medical devices. As demand for compact and efficient actuation solutions grows, SMAs are becoming increasingly popular due to their lightweight nature and unparalleled versatility.
What is an SMA Linear Actuator?
An SMA linear actuator is a device that utilizes the properties of shape memory alloys to create linear motion through thermal activation. When electrical current heats the SMA wire actuator, it transforms into its original shape, generating movement that can be harnessed for various applications. This mechanism allows for precise control in devices ranging from simple mechanisms to complex machinery.
The Versatility of Shape Memory Actuators
Shape memory actuators are incredibly versatile; they can be found in everything from robotics to consumer electronics and even medical devices. Their compact design allows for integration into tight spaces where traditional actuators might struggle or fail altogether. With low power consumption and high reliability, SMA actuators present exciting possibilities for engineers looking to innovate across multiple sectors.
Understanding Shape Memory Alloys
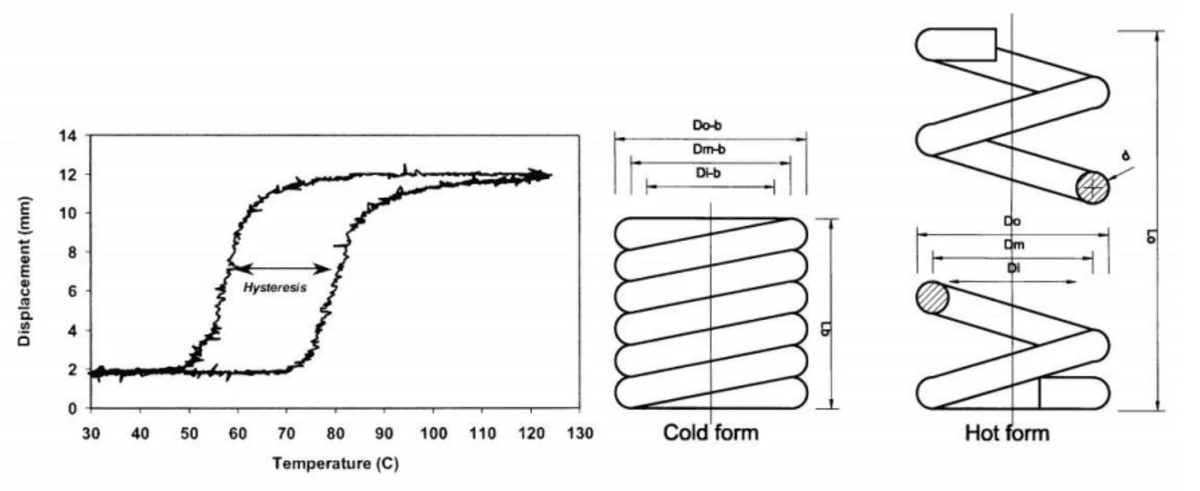
Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) are unique materials with the remarkable ability to return to a predetermined shape when subjected to heat. This phenomenon is primarily due to a specific phase transformation that occurs in these alloys, allowing them to exhibit significant changes in mechanical properties. Among the various types of SMAs, Nitinol—a nickel-titanium alloy—has emerged as a popular choice, especially in the realm of SMA linear actuators.
How SMA Works
At the heart of how an SMA works lies its ability to undergo phase transitions between austenite and martensite states. When an SMA actuator is deformed at lower temperatures (martensitic phase), it retains this shape until it is heated above its transformation temperature, triggering it to revert back to its original form (austenitic phase). This property enables SMA wire actuators and other shape memory actuators to perform mechanical work efficiently without requiring complex mechanisms.
The operational simplicity of an SMA actuator makes it ideal for applications where space and weight are critical factors. For instance, when integrated into devices like robotic fingers or medical devices, these actuators can produce motion by merely applying heat through electrical resistance or environmental changes. The result? A compact solution that delivers impressive performance with minimal components.
The Science Behind Nitinol
Nitinol stands out among SMAs due to its unique combination of superelasticity and shape memory effects. Superelasticity allows Nitinol linear actuators to undergo large strains without permanent deformation when stress is applied within specific temperature ranges. This dual capability makes Nitinol particularly valuable in applications requiring both flexibility and strength.
The scientific principles governing Nitinol involve intricate atomic arrangements that change under varying thermal conditions. When cooled below a certain temperature, the atoms rearrange into a more flexible martensitic structure; heating them restores their rigid austenitic configuration. This atomic dance not only enhances the performance of SMA actuators but also opens doors for innovative designs across various industries.
Applications in Modern Technology
SMA linear actuators have found their way into numerous modern technologies, showcasing their versatility across different fields. In robotics, for instance, these shape memory actuators are used for precise movements in robotic limbs or grippers that mimic human dexterity while maintaining lightweight characteristics essential for mobility. Similarly, in aerospace engineering, companies like GEE SMA leverage Nitinol's properties for deployable structures such as antennas and landing gear mechanisms.
In the medical field, SMAs are revolutionizing device design—from minimally invasive surgical tools that adapt during procedures to stents that expand within blood vessels at body temperature. Their reliability and compact nature make them ideal candidates for applications where traditional motors would be too bulky or power-hungry. As technology continues evolving, we can expect even more inventive uses for these remarkable materials.
Advantages of SMA Linear Actuators

When it comes to the world of actuation, SMA linear actuators stand out for their unique benefits. These shape memory actuators harness the properties of shape memory alloys to provide efficient, reliable movement in a compact design. With their innovative technology, they offer a variety of advantages that make them a compelling choice for numerous applications.
Compact Design and Lightweight
One of the most appealing features of an SMA actuator is its compact design and lightweight nature. Unlike traditional actuators that can be bulky and cumbersome, SMA linear actuators are designed to fit into tight spaces without sacrificing performance. This makes them ideal for applications where weight and space constraints are critical, such as in robotics and aerospace.
The lightweight aspect also means that when integrated into devices like drones or robots, these SMA wire actuators contribute to overall energy efficiency. Less weight translates to lower power requirements, enhancing the device's operational capabilities while maintaining agility. Ultimately, this compactness allows engineers and designers greater freedom when developing innovative solutions.
Low Power Consumption
SMA linear actuators are known for their low power consumption compared to traditional options like electric motors or pneumatic systems. The unique mechanism behind the shape memory actuator allows it to operate effectively at lower energy levels by utilizing thermal activation rather than continuous electrical input. This not only reduces operational costs but also extends battery life in portable applications.
In industries where energy efficiency is paramount—like automotive or aerospace—the low power requirements of nitinol linear actuators can lead to significant savings over time. Moreover, because these SMA actuators only draw power during actuation phases, they minimize wasteful energy expenditure during idle periods. This feature aligns perfectly with modern demands for sustainable technology solutions.
Reliability and Durability
Reliability is key when selecting an actuator for any application, and SMA wire actuators deliver on this front with impressive durability characteristics. Made from robust materials like Nitinol—an alloy known for its resilience—these shape memory actuators can withstand harsh environments without compromising performance. They resist corrosion and fatigue better than many traditional actuator types.
Additionally, the simplicity of their mechanical design means fewer moving parts that could wear out over time; thus enhancing long-term reliability significantly. Users can trust that an SMA actuator will maintain consistent performance throughout its lifespan while requiring minimal maintenance efforts—a win-win situation! In industries ranging from medical devices to robotics, this level of reliability is invaluable.
Comparing SMA Actuators to Traditional Options

As the world of actuators continues to evolve, it's essential to compare SMA linear actuators with traditional options. While conventional actuators have served us well, the unique properties of shape memory actuators present exciting advantages that are difficult to ignore. From performance metrics to cost-effectiveness and industry applications, understanding these differences can help in making informed choices for various projects.
Performance Metrics
When it comes to performance metrics, SMA linear actuators shine in several key areas. Their ability to generate significant force while maintaining a compact design is a standout feature that traditional options often struggle with. Moreover, nitinol linear actuators boast rapid response times and precise control over motion, making them ideal for applications where accuracy is crucial.
In contrast, traditional actuators may require bulky motors and complex gear systems that can lead to inefficiencies and increased wear over time. The simplicity of the shape memory actuator's design not only reduces potential points of failure but also enhances overall reliability. Thus, when considering performance metrics, SMA actuators often outperform their conventional counterparts in both speed and efficiency.
Cost-Effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness is another area where SMA wire actuators can make a compelling case against traditional options. While the initial investment for an SMA actuator may be higher due to advanced materials like nitinol, the long-term savings on energy consumption and maintenance can be substantial. Since these shape memory actuators operate on low power requirements without sacrificing performance, they contribute significantly to reduced operational costs over time.
Additionally, the durability of SMA linear actuators means fewer replacements are needed compared to traditional systems prone to wear and tear. This longevity translates into lower lifecycle costs and less downtime for repairs or replacements—factors that every project manager appreciates when budgeting for new technology. In many cases, investing in SMA technology pays off handsomely down the line.
Use Cases in Various Industries
SMA linear actuators are carving out their niche across various industries thanks to their versatility and unique capabilities. In robotics and automation, these shape memory actuators enable more compact designs while providing reliable motion control—ideal for intricate robotic applications where space is at a premium. Their lightweight nature allows robots equipped with nitinol linear actuators greater agility without compromising power.
The aerospace sector has also embraced SMA technology; companies like GEE SMA are pioneering innovations that leverage these advanced materials for mechanisms requiring precise actuation under extreme conditions. Furthermore, medical devices benefit from the adaptability of shape memory actuators; they can be used in prosthetics or minimally invasive surgical tools where precision movements are paramount for patient safety and comfort.
In summary, as industries continue evolving towards more efficient technologies, it’s clear that integrating SMA wire actuator solutions will open doors previously locked by traditional methods.
Real-World Applications of SMA Linear Actuators

Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) linear actuators are revolutionizing various industries with their unique properties and capabilities. These innovative devices leverage the principles of shape memory alloys, particularly nitinol, to create movement in a compact and efficient manner. From robotics to aerospace and medical applications, SMA actuators are making their mark in the real world.
Robotics and Automation
In the realm of robotics and automation, SMA linear actuators are becoming a game-changer due to their compact design and lightweight nature. Engineers are increasingly integrating shape memory actuators into robotic systems for precise movements without the need for bulky components. The ability of an SMA actuator to convert thermal energy into mechanical motion is particularly advantageous for applications requiring quick response times and reliability.
Moreover, SMA wire actuators offer unique advantages in soft robotics, where flexibility is paramount. Their ability to mimic natural movements allows robots to navigate complex environments more effectively than traditional rigid systems. As automation continues to evolve, the role of SMA linear actuators in enhancing robotic functionalities will only grow stronger.
Aerospace Innovations by GEE SMA
Aerospace technology has seen significant advancements with the introduction of nitinol linear actuators from companies like GEE SMA. These shape memory actuators provide reliable actuation solutions for various aerospace applications, including wing morphing systems and deployable structures. By utilizing an SMA actuator's lightweight design, engineers can reduce overall aircraft weight while maintaining high performance.
GEE SMA's innovations demonstrate how these shape memory alloys can withstand extreme conditions while offering exceptional durability and reliability—a critical requirement in aerospace engineering. The versatility of these devices means they can be adapted for numerous functions within aircraft systems, contributing to enhanced fuel efficiency and operational effectiveness. As this technology continues to develop, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications within the aerospace sector.
Medical Devices and Biomechanics
The medical field is another area where SMA linear actuators shine brightly due to their biocompatibility and precision control capabilities. Shape memory actuators are being used in various medical devices such as stents that expand upon reaching body temperature or prosthetics that adjust dynamically according to user needs. The inherent flexibility offered by an SMA actuator makes it ideal for applications requiring gentle yet effective movement within sensitive environments.
In biomechanics, nitinol wire actuators play a crucial role in developing advanced rehabilitation equipment that aids patients' recovery processes through controlled motion assistance. These devices not only enhance patient comfort but also improve treatment outcomes by providing tailored support during rehabilitation exercises. As research progresses, we anticipate even more innovative uses for shape memory alloys within medical technology that could transform patient care.
Challenges and Considerations

While SMA linear actuators are celebrated for their unique properties, they do come with certain limitations that users should consider. One of the primary challenges is their relatively slow response time compared to traditional actuators. Additionally, the maximum actuation force of an SMA actuator can be lower than that of hydraulic or pneumatic systems, which may limit their application in heavy-duty environments.
Limitations of Shape Memory Actuators
Shape memory actuators, including SMA wire actuators, can struggle with precision when it comes to fine control movements. The temperature range required for activation can also pose a challenge; if the environment doesn't meet these conditions, the performance may suffer significantly. Moreover, while SMA linear actuators are known for their compact design and lightweight features, this often comes at the cost of lower output power compared to traditional options.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of shape memory actuators. Temperature fluctuations can affect the performance and reliability of an SMA actuator; if it operates outside its designated thermal range, it might not function as intended. Furthermore, exposure to moisture or corrosive substances can degrade materials like nitinol used in these devices, making careful consideration essential during application design.
Future Developments in SMA Technology
The future looks bright for shape memory actuator technology as researchers continue to explore innovative solutions to overcome existing limitations. Advancements in material science may lead to more robust versions of nitinol linear actuators that offer improved performance across a broader range of conditions. Additionally, integrating smart technologies into SMA wire actuators could enhance their adaptability and functionality in various applications—from robotics to medical devices—making them even more appealing for future projects.
Conclusion

As we look to the future, the potential of SMA technology is boundless. With ongoing advancements in materials science and engineering, we can expect even more innovative applications for shape memory actuators. From improving efficiency in existing technologies to creating entirely new solutions, SMA linear actuators are poised to play a vital role in various industries.
The Future of SMA Technology
The future of SMA technology hinges on its adaptability and efficiency, with research focusing on enhancing performance metrics like response time and force output. As industries demand more compact and reliable systems, the versatility of SMA actuators will become increasingly valuable. Innovations such as smart materials that can self-heal or change properties based on environmental conditions are on the horizon, making shape memory actuators an exciting field to watch.
GEE SMA's Role in Advancements
GEE SMA is at the forefront of these advancements, pioneering new approaches to harness the unique properties of nitinol linear actuators. By investing in research and development, GEE SMA aims to refine existing technologies while exploring novel applications across sectors like robotics and aerospace. Their commitment not only enhances their product offerings but also contributes significantly to the overall growth of shape memory actuator technology.
Why Choose SMA Linear Actuators for Your Projects
Choosing an SMA linear actuator for your projects means opting for a solution that combines reliability with cutting-edge technology. These sma actuators offer compact designs and low power consumption without sacrificing performance—ideal for modern engineering challenges. Whether you're looking at medical devices or automation systems, integrating a shape memory actuator could elevate your project’s efficiency while ensuring long-term durability.

