Introduction
Nitinol, a unique alloy of nickel and titanium, has gained significant attention in various fields due to its remarkable properties, especially its hardness and superelasticity. Understanding Nitinol hardness is crucial for engineers and designers who utilize this material in applications ranging from medical devices to aerospace components. This introduction sets the stage for exploring how Nitinol's characteristics, including its density of approximately 6,450 kg/m³, influence its performance and market value.
Understanding Nitinol Hardness
Nitinol hardness is a key factor that affects not only the durability but also the functionality of products made from this alloy. The ability to measure Nitinol hardness accurately allows manufacturers to ensure that their products can withstand the rigors of their intended applications without compromising performance. As we delve deeper into Nitinol's structure, we'll discover how variations in composition can lead to differences in hardness, impacting everything from medical implants to everyday items.
The Role of GEE SMA in Nitinol Supply
GEE SMA plays a pivotal role in the supply chain of Nitinol materials, ensuring that high-quality alloys are available for various industries. By focusing on advancements in production techniques and material science, GEE SMA enhances the overall quality and availability of Nitinol wire used across multiple sectors. Their commitment not only influences Nitinol price but also affects the accessibility of innovative solutions that leverage the unique properties of this extraordinary alloy.
Applications of Nitinol in Modern Technology
The versatility of Nitinol makes it an invaluable resource across diverse applications; from medical devices such as stents and guidewires to aerospace innovations where lightweight materials are paramount. With its distinct superelasticity, Nitinol allows for designs that can endure extreme conditions while maintaining functionality—a must-have feature for modern technology. As we explore various uses for this alloy—including specialized products like Nitinol 60—we'll uncover why it continues to be at the forefront of engineering advancements.
What is Nitinol?

Nitinol, a unique alloy of nickel and titanium, is renowned for its remarkable properties that set it apart in the world of materials science. This metal exhibits both shape memory and superelasticity, making it a versatile choice for various applications. Understanding nitinol's structure and characteristics is essential to appreciating its uses and implications across industries.
The Basics of Nitinol Structure
At its core, nitinol's structure is defined by a specific arrangement of nickel and titanium atoms that creates two distinct phases: the austenite phase and the martensite phase. This dual-phase structure is responsible for nitinol's exceptional mechanical properties, including its well-known superelasticity. When subjected to stress, nitinol can undergo reversible transformations between these two phases, allowing it to return to its original shape after deformation—an attribute that directly ties into discussions about nitinol hardness.
Composition and Characteristics
Nitinol typically consists of approximately 55% nickel and 45% titanium by weight; however, variations exist, such as Nitinol 60, which contains a higher nickel content. This specific composition contributes to its unique characteristics like biocompatibility—making it ideal for medical applications—and high fatigue resistance. The interplay between composition and structure plays a crucial role in determining nitinol hardness; different compositions can lead to varying degrees of hardness suitable for diverse applications.
Nitinol Density and Its Implications
The density of nitinol ranges around 6,450 kg/m³, which influences not only its weight but also how it performs under various conditions. This relatively low density allows designers to create lightweight components without sacrificing strength or functionality—key considerations in fields like aerospace where every gram counts. Understanding nitinol density also helps engineers determine how this material will behave when subjected to forces or thermal changes during its use in products such as nitinol wire or other structural components.
Nitinol Hardness Explained

Nitinol hardness is a critical aspect that influences its performance in various applications, from medical devices to aerospace innovations. Understanding how to measure this property can provide valuable insights into the material's suitability for specific uses. Additionally, the interplay between Nitinol density and hardness can lead to significant implications in design and functionality.
Measuring Nitinol Hardness
Measuring nitinol hardness involves various standardized tests, with the Rockwell and Vickers hardness tests being among the most common methods. These tests provide quantifiable data that helps manufacturers determine how well Nitinol wire will withstand stress and deformation under load. Given that nitinol exhibits unique properties such as superelasticity, understanding its hardness is essential for predicting performance in real-world applications.
The results from these measurements are often expressed in terms of a specific scale, which allows for easy comparison with other materials. For example, a higher Rockwell hardness value indicates better resistance to indentation and wear, which is crucial when selecting materials for high-stress environments like aerospace components or surgical instruments. Thus, measuring nitinol hardness not only informs about the material's durability but also aids in cost-effective decision-making regarding Nitinol price.
Factors Influencing Hardness
Several factors influence nitinol hardness, including composition, processing methods, and heat treatment processes. Variations in nickel content can significantly alter the alloy's mechanical properties; therefore, maintaining precise control over composition is vital for achieving desired characteristics like increased strength or improved superelasticity. Additionally, different manufacturing techniques can lead to variations in microstructure that directly affect hardness levels.
Heat treatment plays a crucial role as well; it can enhance or reduce nitinol hardness depending on the temperature and duration of exposure during processing. For instance, aging treatments can increase strength while potentially compromising ductility if not performed correctly. Consequently, understanding these factors allows manufacturers to tailor Nitinol 60 specifically for diverse applications by optimizing its mechanical properties.
Importance of Hardness in Applications
The importance of nitinol hardness cannot be overstated when it comes to its applications across various industries. In medical settings where reliability is paramount—such as stents or guidewires—hardness contributes directly to performance longevity under physiological conditions. Similarly, aerospace innovations rely on hard yet lightweight materials; thus, understanding how nitinol density kg m3 relates to its hardness becomes essential for engineers looking to push boundaries without compromising safety.
Moreover, everyday products utilizing Nitinol superelasticity benefit from an optimal balance between flexibility and strength achieved through careful manipulation of their inherent properties—including hardness levels. As industries continue evolving towards more advanced technologies involving smart materials like nitinol wire, recognizing how these attributes interact will be key in driving innovation forward while also keeping an eye on overall costs associated with Nitinol price fluctuations.
Nitinol Price Factors
When considering the price of Nitinol, several factors come into play that can significantly influence its market value. The unique properties of Nitinol, including its superelasticity and shape memory effects, make it a sought-after material in various industries, from medical devices to aerospace applications. Understanding these price factors is essential for businesses looking to incorporate Nitinol wire or other forms into their projects.
Market Influences on Nitinol Pricing
The pricing of Nitinol is greatly affected by market demand and supply dynamics. As industries continue to explore innovative uses for Nitinol—particularly in medical applications and high-tech sectors—the demand has surged, driving prices upward. Additionally, fluctuations in raw material costs and production capabilities can impact the overall pricing structure of Nitinol products.
Another significant aspect affecting pricing is the competition among suppliers, particularly those specializing in specific types like Nitinol 60. The availability of different grades with varying hardness levels also plays a role; harder variants may command higher prices due to their enhanced performance characteristics. Therefore, businesses must stay informed about market trends to effectively budget for their projects involving this versatile alloy.
Cost Comparisons with Other Alloys
When comparing the cost of Nitinol with other alloys, it's crucial to consider both initial investment and long-term benefits. While the upfront price of Nitinol may be higher than that of traditional metals like stainless steel or titanium, its unique properties often justify the expense over time due to reduced maintenance costs and enhanced performance—especially in applications requiring high levels of nitinol hardness or superelasticity.
Moreover, when analyzing density—Nitinol typically has a density around 6,450 kg/m³—it becomes evident that this alloy provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratios compared to many alternatives. This characteristic can lead to significant savings in industries such as aerospace where weight reduction is critical for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Thus, while initial costs may appear daunting, the long-term advantages make a compelling case for choosing Nitinol over conventional materials.
Budgeting for Nitinol Projects
Budgeting effectively for projects involving Nitinol requires careful consideration of various factors beyond just material cost. It's essential to account for additional expenses such as processing fees and potential design adaptations needed due to the unique properties inherent in the nitinol structure. By factoring these elements into project budgets upfront, organizations can avoid unpleasant surprises down the line.
Furthermore, understanding specific project requirements related to nitinol hardness will help determine which grade is necessary—this choice directly influences overall expenditure as well. For instance, opting for specialized grades like Nitinol 60 might incur higher costs initially but could yield greater returns through improved functionality in demanding applications such as medical implants or aerospace components. Ultimately, thorough planning ensures that businesses maximize their investment while leveraging all available benefits offered by this remarkable alloy.
Exploring Nitinol Uses
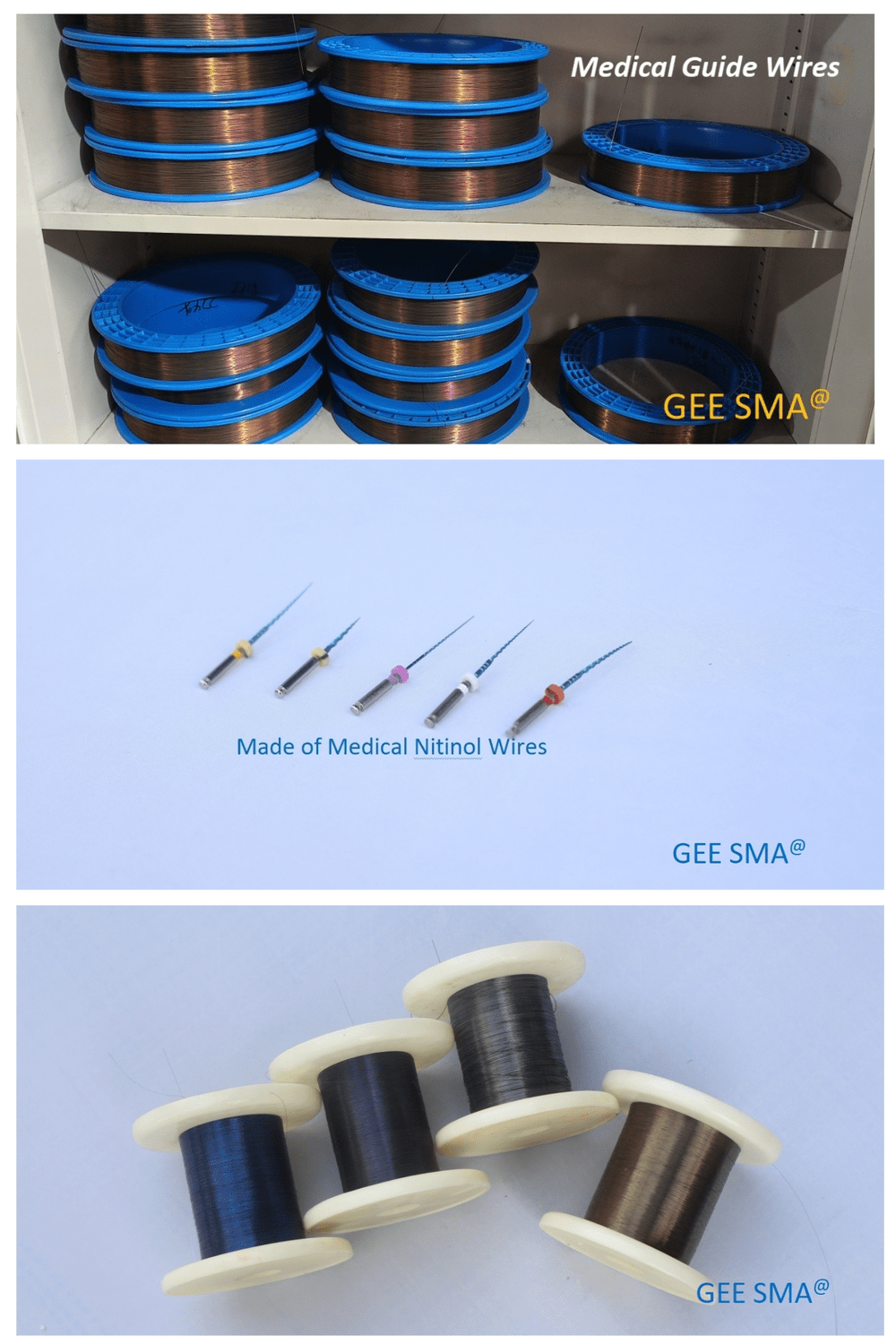

Nitinol, a remarkable alloy of nickel and titanium, has carved out a niche in various industries due to its unique properties. Its exceptional hardness and superelasticity make it an ideal candidate for applications ranging from medical devices to aerospace innovations. Understanding the myriad uses of Nitinol not only highlights its versatility but also showcases its significance in modern technology.
Medical Applications of Nitinol Wire
One of the most prominent uses of Nitinol wire is in the medical field, where its superelasticity and biocompatibility shine brightly. This alloy is extensively utilized in stents, guidewires, and other critical surgical instruments thanks to its ability to return to a predetermined shape when heated—an essential feature for minimally invasive procedures. The hardness of Nitinol wire ensures durability while maintaining flexibility, making it perfect for navigating the complex human anatomy without causing damage.
Nitinol’s unique structure allows it to withstand significant stress without permanent deformation, which is crucial during surgeries where precision is key. Additionally, the density of Nitinol at approximately 6,450 kg/m³ contributes to its lightweight nature, enhancing patient comfort during procedures that involve implanted devices. As medical technology advances, the demand for high-performance materials like Nitinol continues to grow exponentially.
Aerospace Innovations with Nitinol
The aerospace industry has also recognized the potential of Nitinol due to its impressive strength-to-weight ratio and fatigue resistance. Components made from this alloy can endure extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity—essential for aircraft safety and performance. Engineers are increasingly leveraging the unique properties of Nitinol 60 in applications such as actuators and sensors that require reliable operation under fluctuating temperatures.
Moreover, innovations involving Nitinol are paving the way for lighter aircraft designs that consume less fuel—a critical factor in reducing operational costs and environmental impact. The combination of low density (around 6,450 kg/m³) and high hardness makes it an attractive option compared to traditional materials used in aerospace applications. As research continues into advanced alloys like Nitinol 60, we can expect even more groundbreaking developments on the horizon.
Everyday Products Utilizing Nitinol Superelasticity
Beyond specialized industries like medicine and aerospace, everyday products are also reaping the benefits of Nitinol's extraordinary qualities. From eyeglass frames that bend without breaking to innovative dental braces that adjust comfortably over time—Nitinol's superelasticity enhances user experience across various consumer goods. These products not only showcase practical uses but also highlight how this alloy can improve daily life through superior performance.
The affordability aspect cannot be overlooked either; while initial costs may seem high due to factors influencing Nitinol price fluctuations in global markets, long-term savings often outweigh upfront investments thanks to reduced maintenance needs and increased durability associated with high hardness levels. Additionally, as manufacturers continue exploring new ways to incorporate this versatile material into their designs, we can anticipate even more exciting applications emerging on store shelves soon.
The Significance of Nitinol 60

Nitinol 60 is a specialized variant of Nitinol that boasts unique properties, making it particularly valuable in various industries. This alloy's composition leads to enhanced performance characteristics, such as improved superelasticity and fatigue resistance. Understanding the properties of Nitinol 60 can help manufacturers leverage its advantages for innovative applications.
Properties of Nitinol 60
Nitinol 60 exhibits remarkable hardness compared to other forms of Nitinol, which contributes significantly to its versatility in demanding environments. Its density, approximately 6,500 kg/m³, ensures it remains lightweight while maintaining structural integrity under stress. Additionally, the unique Nitinol structure allows for exceptional shape memory effects and superelasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility without permanent deformation.
Applications in Industry
The applications of Nitinol 60 span across multiple sectors including medical devices, aerospace engineering, and consumer products. In the medical field, Nitinol wire is often utilized in stents and guidewires due to its biocompatibility and ability to return to predefined shapes after deformation—a testament to its superior nitinol hardness. Aerospace innovations benefit from this alloy's lightweight nature combined with high strength-to-weight ratios, critical for enhancing fuel efficiency and performance.
Why Choose Nitinol 60?
Choosing Nitinol 60 over other alloys can lead to significant advantages in terms of performance and longevity in products designed for extreme conditions. Its superior hardness translates into greater durability and less wear over time compared to alternatives—ideal for projects where reliability is paramount. Furthermore, understanding the implications of nitinol price helps companies budget effectively while still investing in high-quality materials like Nitinol 60 that promise innovation and efficiency.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of Nitinol, it's clear that this remarkable alloy is not just a scientific curiosity but a game-changer across various industries. From its unique Nitinol structure that allows for superelasticity to its practical applications in medicine and aerospace, innovations driven by GEE SMA are pushing the boundaries of what we thought possible. As we look forward, the continued development and refinement of Nitinol will likely lead to even more groundbreaking uses and enhanced performance characteristics.
Innovations Driven by GEE SMA
GEE SMA has been at the forefront of harnessing Nitinol's properties, particularly focusing on improving Nitinol hardness for various applications. By optimizing the alloy’s composition and processing methods, they have made strides in enhancing its performance while keeping an eye on cost-effectiveness—essential when considering Nitinol price factors in competitive markets. As industries increasingly adopt Nitinol wire for innovative solutions, GEE SMA's commitment to quality and innovation ensures they remain a key player in shaping future advancements.
The Future of Nitinol Technology
Looking ahead, the future of Nitinol technology appears bright with endless possibilities for innovation. Research into advanced formulations like Nitinol 60 promises to unlock even more potential applications while maintaining desirable characteristics such as density (around 6,500 kg/m³) and superelasticity. As manufacturers continue to explore new uses for this versatile alloy—from medical devices that require precise flexibility to aerospace components demanding high strength—the demand for high-quality materials will only grow.
Choosing the Right Nitinol Supplier
When it comes to selecting a reliable supplier for your Nitinol needs, several factors should be taken into account beyond just pricing or availability. Look for suppliers who demonstrate expertise in managing nitinol hardness and can provide detailed specifications about their products—this includes understanding how different compositions can affect performance in specific applications. Ultimately, choosing a reputable supplier who prioritizes quality assurance will ensure that your projects benefit from optimal material properties like those found in high-grade Nitinol wire.

